Wayanad landslides: Cabinet nod to remove debris accumulated in the Punnapuzha river
Punnapuzha River:
-
A tributary of the Chaliyar River.
-
Flows through parts of Kerala in South India.
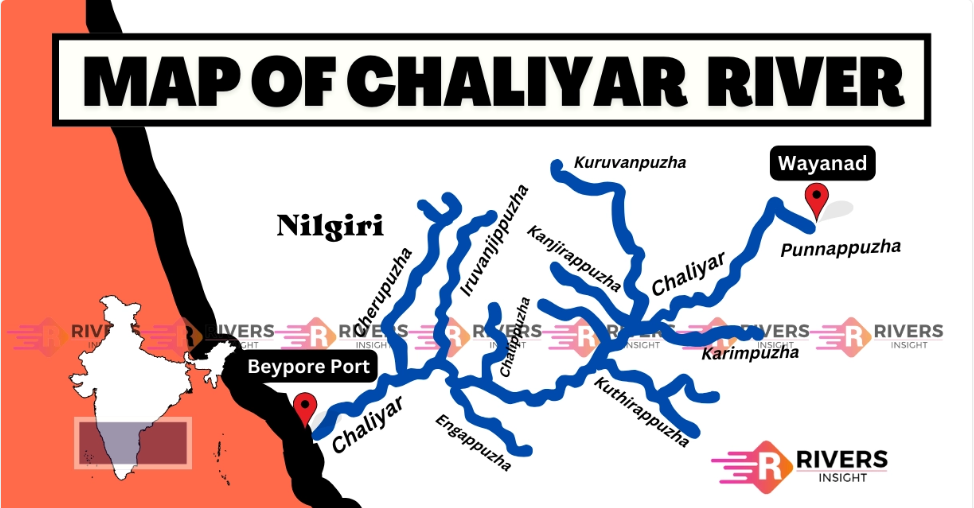
Chaliyar River of Kerala
Basic Facts:
-
Other Names: Chulika River, Nilambur River, Beypore River
-
Length: 169 km (4th longest in Kerala)
-
States/Districts: Flows through Malappuram and Kozhikode districts
-
Final Destination: Empties into the Arabian Sea at Beypore Port, near Chaliyam Harbour
Origin & Course:
-
Origin: Ilambaleri Hills, Nilgiri Mountains (near Wayanad–Malappuram border)
-
Course:
-
Flows primarily southward through Malappuram district
-
Forms part of the district boundary with Kozhikode for ~17 km
-
Final 10 km: Flows through Kozhikode city before reaching Lakshadweep Sea via an azhi (estuary)
-
Major Towns Along the River:
-
Upstream: Nilambur, Mampad, Perakamanna
-
Midstream: Areekode, Vazhakkad, Cheruvadi, Kavanoor
-
Downstream: Mavoor, Feroke, Beypore
Tributaries:
-
Major Streams:
-
Punnapuzha
-
Chaliyarpuzha
-
Kanjirapuzha
-
Karimpuzha
-
Iruvahnipuzha
-
Thottumukkampuzha
-
-
Other Tributaries: Kurumanpuzha, Pandipuzha, Maradipuzha, Kuthirapuzha, Karakkodupuzha
-
Origin of tributaries: Nilgiri Hills (east) and Wayanad Hills (north)
Waterfalls Near the Source:
-
Meenmutty Falls:
-
Near Vaduvanchal, Wayanad
-
One of the highest waterfalls in Kerala
-
Acts as a primary source of the Chaliyar
-
-
Soochipara Falls:
-
Located in Chullikka River (tributary of Chaliyar)
-
Known for its three-tiered drop and scenic forests
-
Ecological & Economic Significance:
-
Natural Gold Fields:
-
Found in Nilambur valley
-
Estimated 2.5 million cubic meters of placer deposits with 0.1 g/m³ of gold
-
-
Historical Timber Trade Route:
-
Timber (especially teak and rosewood) transported from Nilambur to Kallai during monsoon using river rafts
-
Kallai (Kozhikode) was a global timber hub in the 19th–20th century
-
-
Pollution & Environmental Action:
-
Pulp factory at Mavoor caused major river pollution
-
K. A. Rahman led the cleanup agitation (1999), forming the Paristhithi Samrakshana Samithi
-
Key Features:
-
Does not dry up in the dry season (unlike many Kerala rivers)
-
Important for biodiversity, local livelihoods, and inland navigation
