Neutrinos – Properties, Discovery, and Origins
What are Neutrinos?
-
Neutrinos (symbol: ν) are electrically neutral, elementary particles that interact only via the weak force and gravity.
-
They do not interact via the strong or electromagnetic forces, allowing them to pass through matter virtually undetected.
Key Properties:
-
Neutrinos have very small mass — once thought to be zero.
-
They are fermions with spin ½ ħ.
-
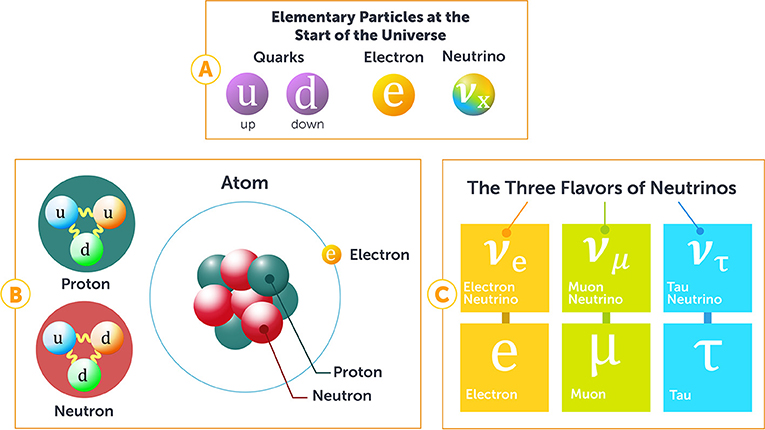
Neutrinos come in three types (flavors):
-
Electron neutrino (νₑ)
-
Muon neutrino (ν_μ)
-
Tau neutrino (ν_τ)
-
-
Each flavor is linked with a corresponding charged lepton.
Flavor Oscillation:
-
Neutrinos can oscillate between different flavors during flight.
-
This means a neutrino created as νₑ may later behave as ν_μ or ν_τ — a quantum superposition of mass states.
-
This proves they have mass, but the exact mass values remain unknown (only mass differences and upper limits are known).
Antineutrinos:
-
Every neutrino has a corresponding antiparticle (antineutrino), also electrically neutral but with:
-
Opposite lepton number and weak isospin
-
Right-handed chirality (vs. left-handed for neutrinos)
-
Production Sources:
-
Neutrinos are produced in:
-
Beta decay of nuclei or hadrons
-
Nuclear reactions in stars (e.g., Sun), reactors, and accelerators
-
Supernovae, cosmic ray interactions, and neutron star activity
-
-
Earth receives a solar neutrino flux of ~65 billion neutrinos per second per cm².
Historical Context:
-
Proposed in 1930 by Wolfgang Pauli to explain conservation in beta decay.
-
Pauli initially called it a "neutron", before the actual neutron was discovered by James Chadwick in 1932.
-
The term “neutrino” (Italian for “little neutral one”) was coined by Edoardo Amaldi and popularized by Enrico Fermi to distinguish it from Chadwick’s neutron.
Applications:
-
Neutrinos are used in Earth tomography and offer insights into cosmic events.
-
Their elusive nature and unique properties make them key to understanding physics beyond the Standard Model.
