Ahmedabad Air India Crash – "DNA Profiling" Nearly Complete
What is DNA Profiling?
DNA profiling is a scientific method used to identify a person based on their unique DNA.
-
Just like everyone has a unique fingerprint, everyone (except identical twins) has unique DNA.
-
DNA is found in cells (like blood, hair, saliva, skin).
-
A small part of DNA has patterns that are unique to every individual.
-
These unique patterns are studied to match or identify a person.
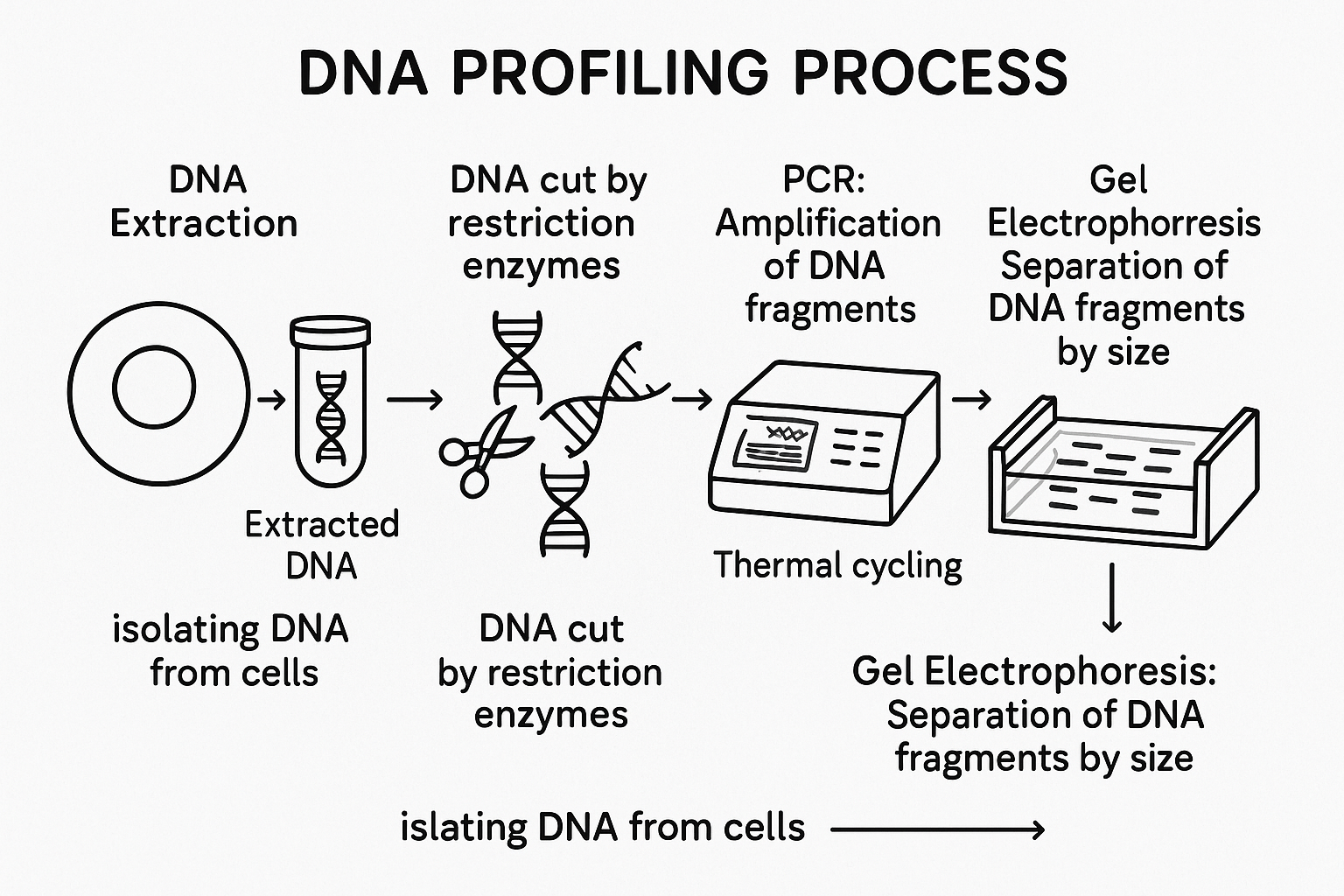
Process of DNA Profiling (Step-by-step )
-
Sample Collection:
-
DNA is taken from sources like blood, saliva, semen, hair, or bones.
-
-
DNA Extraction:
-
DNA is separated and purified from the sample.
-
-
Amplification (PCR):
-
Using a technique called PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction), specific DNA regions are copied many times to make enough to study.
-
-
Fragment Analysis:
-
Special parts of DNA (called STRs – Short Tandem Repeats) are analyzed, which differ from person to person.
-
-
DNA Profile Creation:
-
A graph or pattern is generated showing the DNA features of the person.
-
-
Comparison/Matching:
-
The profile is compared with others — for example, to match a crime suspect, find missing persons, or establish parentage.
-
UPSC Prelims Points:
-
DNA Profiling = Technique to identify individuals using DNA.
-
PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) = Used to amplify DNA.
-
STRs (Short Tandem Repeats) = Part of DNA used for comparison.
-
Applications:
-
Forensic investigations
-
Disaster victim identification
-
Paternity testing
-
Missing persons tracing
-
DNA is not present in ribosomes – Ribosomes are composed of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and proteins, not DNA.(also Human RBC don't have DNA)
DNA’s Role: Stores genetic instructions for building and maintaining an organism.
Ribosomes’ Role: Synthesize proteins using mRNA (transcribed from DNA).
Where DNA is Found:
Nucleus (primary location in eukaryotic cells).
Mitochondria (have their own DNA).
Chloroplasts (in plant cells, contain their own DNA).
While DNA provides the genetic code, ribosomes (which lack DNA) translate that code into proteins.
DNA is not present in ribosomes – Ribosomes are composed of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and proteins, not DNA.(also Human RBC don't have DNA)
DNA’s Role: Stores genetic instructions for building and maintaining an organism.
Ribosomes’ Role: Synthesize proteins using mRNA (transcribed from DNA).
Where DNA is Found:
Nucleus (primary location in eukaryotic cells).
Mitochondria (have their own DNA).
Chloroplasts (in plant cells, contain their own DNA).
While DNA provides the genetic code, ribosomes (which lack DNA) translate that code into proteins.
Is DNA Found in Red Blood Cells (RBCs)?
Mature RBCs (in humans & mammals): No DNA
They lose their nucleus and organelles (including mitochondria) during maturation to maximize hemoglobin content for oxygen transport.
Since they lack a nucleus and mitochondria, they do not contain any DNA.
Immature RBCs (reticulocytes): Temporarily retain some organelles
Early-stage RBCs still have ribosomal RNA (rRNA) but no nuclear DNA.
Any remaining DNA fragments are degraded before full maturation.
Exceptions:
Birds & some reptiles have nucleated RBCs (contain DNA).
Fetal RBCs in early development (in mammals) may briefly contain nuclei.
Mature RBCs (in humans & mammals): No DNA
They lose their nucleus and organelles (including mitochondria) during maturation to maximize hemoglobin content for oxygen transport.
Since they lack a nucleus and mitochondria, they do not contain any DNA.
Immature RBCs (reticulocytes): Temporarily retain some organelles
Early-stage RBCs still have ribosomal RNA (rRNA) but no nuclear DNA.
Any remaining DNA fragments are degraded before full maturation.
Exceptions:
Birds & some reptiles have nucleated RBCs (contain DNA).
Fetal RBCs in early development (in mammals) may briefly contain nuclei.
Mature human red blood cells do not contain DNA, making them useful in DNA forensics (since any DNA in blood samples comes from white blood cells, not RBCs).
Mature human red blood cells do not contain DNA, making them useful in DNA forensics (since any DNA in blood samples comes from white blood cells, not RBCs).
