Flue Gas Desulphurisation (FGD) Units
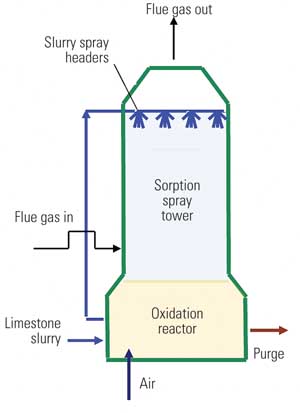
1. What is FGD?
Purpose: Removes sulphur dioxide (SO₂) from flue gas emitted by coal-fired thermal power plants (TPPs).
Methods:
Wet Limestone FGD (most common, produces gypsum for construction).
Dry Sorbent Injection (uses powdered limestone).
Seawater FGD (for coastal plants, neutralizes SO₂ before discharge).
2. Why is SO₂ Harmful?
Environmental Impact:
Contributes to global warming.
Forms secondary PM2.5 (15% of India’s PM2.5 linked to coal plants).
Health Impact: Causes respiratory diseases and acid rain.
3. Status of FGD in India
2015 Policy: Mandated FGD in 537 coal TPPs (deadline extended multiple times).
Current Compliance (2025): Only 39 out of 537 plants installed FGD.
New Recommendations:
PSA Committee (Principal Scientific Advisor) (2025) suggests rolling back mandatory FGDs due to high costs.
MoEFCC extended deadlines (2027-2029) without clear justification.
4. Challenges & Controversies
High Costs:
₹1.2 crore/MW installation cost (~₹97,000 crore for 97,000 MW new capacity).
Tariff Impact: Adds ₹0.72/kWh (mostly fixed costs).
Alternatives?
None exist for SO₂ removal; experts insist FGD is essential for clean air.
Regional Impact:
PM2.5 contribution varies (e.g., Delhi less affected than cities near plants).
5. Government’s Dilemma
Power Minister’s Stance: Balancing costs vs. health/environmental risks.
Experts’ View: Delaying FGDs risks public health and air quality goals.
Why Relevant for UPSC?
Prelims (Environment & Pollution Control)
Keywords: FGD, SO₂, PM2.5, Wet Limestone Method, PSA Committee.
Data Points: 537 coal plants, 39 FGDs installed, ₹1.2 crore/MW cost.
Mains (GS-3: Environmental Pollution & Energy)
Potential Questions:
"Critically examine India’s struggle to implement FGDs in coal power plants."
"Can India achieve its clean air targets without FGDs? Discuss alternatives."
Key Points
- FGDs are vital for reducing SO₂ but face delays due to high costs.
- India’s compliance is poor (only 7% plants installed FGDs).
- Experts warn rolling back FGDs will worsen air pollution and health risks.
- No viable alternative exists; debate centers on cost vs. environmental priorities.
