Enhanced Rock Weathering (ERW) for Climate Mitigation
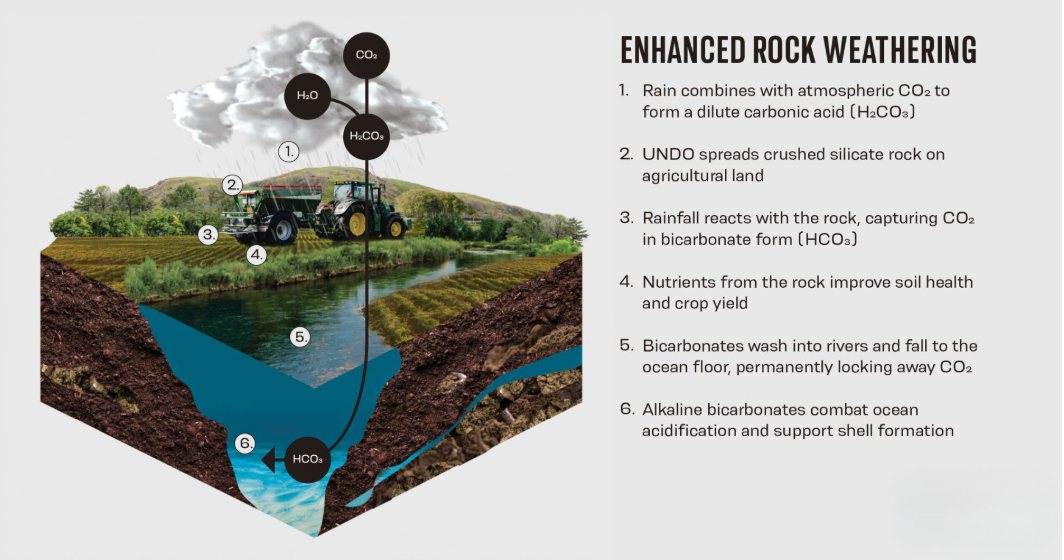
Enhanced Rock Weathering (ERW)
What is ERW?
Enhanced Rock Weathering (ERW) is a carbon dioxide removal (CDR) technique that accelerates the natural process of rock weathering to capture and store atmospheric CO₂ in a stable form for thousands to millions of years.
Natural Process Behind ERW:
-
CO₂ + Rainwater → Carbonic Acid
-
Carbonic Acid + Rocks → Bicarbonates (which eventually form limestone, storing carbon for geological timescales)
-
This natural process is slow, taking centuries to remove meaningful amounts of CO₂.
How ERW Works:
-
Rocks like basalt or wollastonite are crushed into fine powder.
-
This powder is spread on agricultural land.
-
The increased surface area of finely ground rocks accelerates chemical reactions with CO₂ in rainwater and soil.
-
Carbon is locked up as bicarbonate, stored for 100,000+ years.
ERW speeds this up using fast-weathering rocks with increased surface area through fine grinding.
Why Use Agricultural Land for ERW?
-
Co-benefits to farmers:
-
Releases essential nutrients (magnesium, calcium, potassium, phosphorus)
-
Improves soil health and pH
-
Reduces fertilizer dependency
-
-
Supports climate-resilient agriculture and offers free soil amendments to farmers.
Climate Significance:
-
IPCC Target: To avoid catastrophic climate change, we must remove 10 billion tonnes of CO₂/year by 2050.
-
ERW Potential: Can contribute up to 4 billion tonnes/year, covering 40% of the global removal target.
Scientific Challenges and Concerns:
-
Actual CO₂ Removal Rates Vary: A U.S. study showed 10.5 tonnes CO₂/ha/year removal; trials in Malaysia and Australia showed much lower rates.
-
Depends on:
-
Rock type and grain size
-
Temperature and rainfall
-
Soil pH and microbial activity
-
Farming practices
-
-
Measurement Issues:
-
Popular metric: Cation release from rocks (e.g. Ca²⁺, Mg²⁺)
-
Problem: Cations are released regardless of which acid (carbonic or stronger) caused weathering, leading to overestimation of CO₂ capture.
-
Recent Developments:
UNDO–Microsoft Partnership (2024–25)
Highlights:
-
Microsoft funds UNDO’s scientific ERW trials in Canada and the UK.
-
Trials at:
-
University of Guelph farm (Ontario)
-
Newcastle University farm (UK)
-
-
Purpose: Improve Monitoring, Reporting and Verification (MRV) of carbon removal.
Scientific Importance:
-
Focus on wollastonite, a fast-weathering mineral, enabling quicker data generation.
-
Emphasis on field-level MRV accuracy for open environmental systems.
-
Helps move ERW toward scalable, verifiable carbon removal technology.
Canada as a Strategic Hub:
-
Canadian government’s Net Zero by 2050 commitment
-
Canada hosts 70+ CDR companies
-
UNDO working with Canadian Wollastonite to supply minerals and verify carbon capture
