Initiate proceedings to elect Deputy Speaker, says Kharge in letter to PM Modi
Deputy Speaker of Lok Sabha
🔷 Why in News
The post of Deputy Speaker has remained vacant throughout the 17th Lok Sabha and continues to be unfilled in the 18th Lok Sabha.
Congress president Mallikarjun Kharge wrote to the Prime Minister demanding the election of the Deputy Speaker, citing constitutional violation.
Highlights growing concerns over adherence to democratic norms and institutional functioning.
🔷 Constitutional Provisions
| Article | Provision |
|---|---|
| Article 93 | Lok Sabha shall elect both Speaker and Deputy Speaker “as soon as may be”. |
| Article 94 | Deals with vacation, resignation, and removal of Speaker and Deputy Speaker. |
| Article 95(1) | Deputy Speaker performs duties of Speaker during absence or vacancy and exercises the same powers. |
| Article 178 | Corresponding provision for State Assemblies. |
Note: No separate oath is required for Deputy Speaker; MP's oath under Third Schedule is sufficient.
🔷 Election Process
Governed by Rule 8 of Rules of Procedure and Conduct of Business in Lok Sabha.
Elected by simple majority of members present and voting.
Usually held in the second session, but can be in the first session of the new Lok Sabha or Assembly.
Speaker fixes the date for the election.
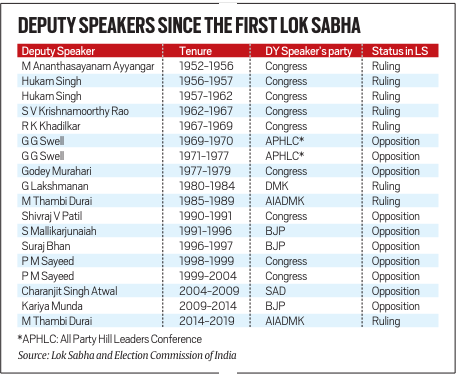
Post is traditionally offered to the Opposition (1990–2014).
No Deputy Speaker during 1997–1998 and the entire 17th Lok Sabha (2019–2024).
The Constitution does not specify a time frame, allowing governments to delay or avoid the appointment.
🔷 Tenure & Removal
The Deputy Speaker holds office during the life of the Lok Sabha or until:
Ceases to be a member
Resigns to the Speaker
Removed by absolute majority (i.e., majority of the total strength) with 14 days’ prior notice
🔷 Historical Background – Speaker & Deputy Speaker
Created under the Government of India Act, 1919 (effective from 1921).
Prior to 1921, the Governor-General presided over the Central Legislative Council.
First Speaker: Frederick Whyte
First Deputy Speaker: Sachidanand Sinha
1925: Vithalbhai J. Patel became the first Indian and first elected Speaker.
Government of India Act, 1935 renamed the posts as Speaker and Deputy Speaker, though older terms remained until 1947.
1956: G.V. Mavalankar died in office; Deputy Speaker M. Ananthasayanam Ayyangar served as Acting Speaker.
2002: After Speaker G.M.C. Balayogi’s death, Deputy Speaker P.M. Sayeed presided until Manohar Joshi was elected.
🟣 Mains Perspective
Significance of the Office
1. Legislative Continuity
Presides over Lok Sabha in the Speaker's absence, ensuring uninterrupted proceedings.
2. Constitutional Authority
Holds an independent constitutional office, not subordinate to the Speaker. Participates in important committees like the Rules Committee.
3. Neutral and Impartial Role
Expected to operate above party politics, reinforcing impartiality and trust in parliamentary functioning.
4. Democratic Inclusion and Consensus Building
Though not mandated, the post is traditionally held by the Opposition, ensuring bipartisan representation and promoting consensual politics.
5. Committee Leadership
Automatically becomes Chairperson of Parliamentary Committees when appointed to them.
Concerns and Current Issues
Vacant in both 17th and 18th Lok Sabha, despite being a constitutional mandate under Article 93.
No specific time frame in Constitution leads to indefinite delays in appointment.
Reflects growing centralisation of power and decline of parliamentary conventions.
Reforms and Safeguards Suggested
1. Mandated Timeline for Election
Amend the Constitution or Rules of Procedure to require election within 30 days of the first sitting of Lok Sabha.
2. Empowering the President
Introduce a statutory provision empowering the President (on PM's advice) to initiate the election process if unduly delayed.
3. Regular Delegation of Duties
Institutionalise the Deputy Speaker's role, even during the Speaker's presence, to reinforce functional relevance.
4. Codification of Powers
Define Deputy Speaker’s role via statutory framework or updated rules to ensure neutrality and clarity, limiting executive overreach.
Broader Relevance for UPSC GS-II
Strengthens Parliamentary Democracy and ensures smooth legislative functioning
Acts as a check and balance within the legislature
Reflects principles of Separation of Powers and Inclusivity in Governance
Contributes to accountability and institutional trust in democratic processes
