Strait of Hormuz: Strategic Importance and Current Threats
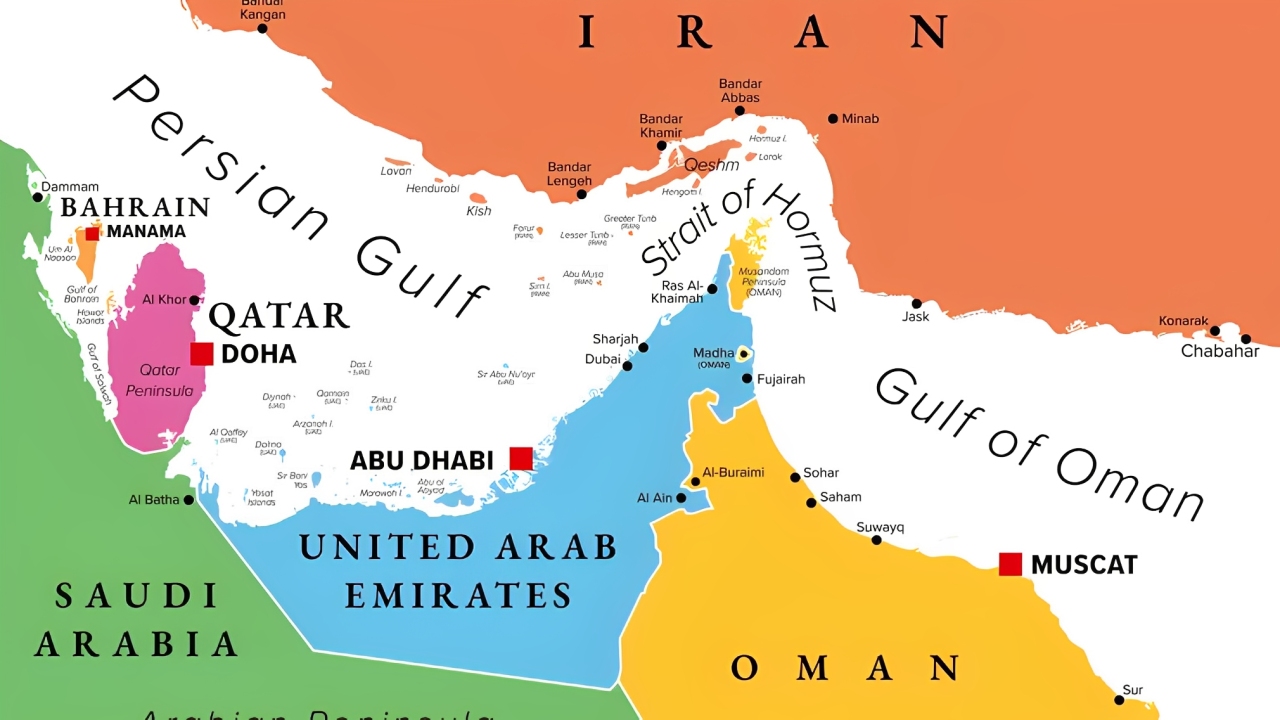
What is the Strait of Hormuz?
-
A narrow waterway (55–95 km wide) between Iran and the Arabian Peninsula, linking the Persian Gulf with the Gulf of Oman and Arabian Sea.
-
It is the world’s most critical oil chokepoint, with ~20 million barrels of oil per day passing through in 2024 — about 25% of global oil trade.
-
Key exporters using it: Saudi Arabia, Iraq, Kuwait, UAE, Qatar, and Iran.
Why is the Strait in News ?
-
Escalating Iran-Israel conflict following:
-
Israel's bombing of Iranian nuclear and military sites (June 13, 2025).
-
Iranian missile retaliation.
-
-
Fears that Iran may block or disrupt the strait — affecting global oil and gas supply chains.
Historical Precedents
-
1980–88 Iran-Iraq War: Known as the Tanker War — attacks on oil tankers led to U.S. military escort of Kuwaiti ships.
-
2011–12: Iran threatened to block the Strait over Western sanctions.
-
2019: Tensions after U.S. exit from the nuclear deal; Iran seized UK’s oil tanker Stena Impero and shot down a U.S. drone.
Current Impact and Response
-
Oil Price Volatility:
-
Brent crude rose briefly post-conflict but later dipped to $77.01/barrel.
-
-
Shipping Risks:
-
Risk of delays, higher insurance, and logistics costs.
-
Alternative Supply Routes
-
Land Pipelines:
-
Saudi Arabia (ARAMCO) and UAE pipelines bypass the Strait.
-
Iran's Goreh–Jask pipeline to Gulf of Oman offers partial bypass.
-
-
However, sea routes via the Strait remain indispensable.
India’s Exposure and Strategy
-
India’s dependence:
-
40% of crude oil and 54% of LNG imports pass through the Strait.
-
1.5 million barrels/day (of India’s 5.5 million daily oil use) pass through it.
-
-
Contingency Plans:
-
Government may consider West African oil imports to mitigate risks.
-
OPEC+ production cuts since 2022 have marginally reduced oil flows via the Strait.
-
80% of the oil shipped through the Strait is destined for Asian countries.
