BIOCHAR: POTENTIAL AND PATHWAY FOR INDIA
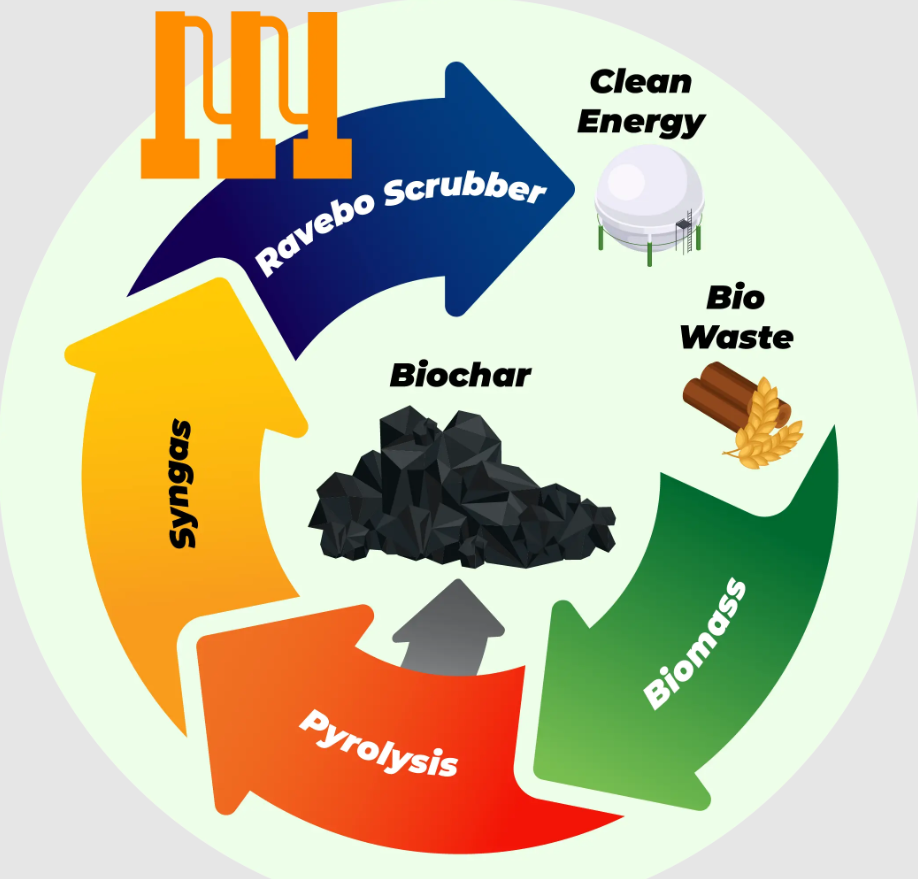
What is Biochar?
-
A carbon-rich, stable form of charcoal produced via pyrolysis of biomass (agricultural residue or organic municipal solid waste) under limited oxygen.
-
Acts as a carbon sink, soil amendment, and a multipurpose byproduct producer.
Potential of Biochar in India
-
Biomass availability:
-
600+ million tonnes of agri-residue annually.
-
60+ million tonnes of municipal solid waste.
-
-
Current issues: Open burning and landfills lead to emissions of CO₂, CH₄, N₂O and air pollutants.
-
Carbon removal potential:
-
30-50% of surplus waste → 15-26 million tonnes of biochar
-
Removes 0.1 gigatonnes CO₂-equivalent/year.
-
Byproducts and Energy Potential
A. Syngas (20–30 million tonnes)
-
Can produce 8–13 TWh of electricity (~0.5–0.7% of India’s annual power).
-
Can replace 0.4–0.7 million tonnes of coal annually.
Main pollutions in the syngas that can be eliminated with a scrubber can be classified as:
- Fine dust (solid particulate matter)
- Alkali compounds
- Nitrogen compounds
- Tar
- Light hydrocarbons (methane, ethane)
- Heavy hydrocarbon
B. Bio-oil (24–40 million tonnes)
-
Can substitute 12–19 million tonnes of diesel/kerosene (~8%).
-
Reduces crude oil imports and 2% of total fossil-fuel-based emissions.
Biochar as a Carbon Sink
-
Stability: Stores carbon for 100–1,000 years.
-
Mitigates:
-
Nitrous oxide emissions by 30–50% in agriculture.
-
High GWP: N₂O is 273x more potent than CO₂.
-
Applications Across Sectors
A. Agriculture
-
Enhances soil organic carbon, water retention, soil fertility.
-
Reduces fertilizer need by 10–20%, increases crop yield by 10–25%.
B. Construction Sector
-
Add 2–5% biochar in concrete:
-
Improves mechanical strength.
-
Increases heat resistance by 20%.
-
Captures 115 kg CO₂/m³.
-
Makes construction a carbon sink.
-
C. Wastewater Treatment
-
1 kg biochar + additives can treat 200–500 litres of wastewater.
-
India’s untreated wastewater: ~72% of 70 billion litres/day.
-
Demand potential: 2.5–6.3 million tonnes of biochar/year.
D. Carbon Capture
-
Modified biochar can adsorb CO₂ from industrial exhausts.
-
Less efficient than conventional CCS methods but more sustainable.
Challenges in Scaling Biochar
A. Market & Policy Gaps
-
Not integrated in carbon credit systems due to:
-
Lack of standard feedstock market.
-
Inconsistent carbon accounting.
-
Weak MRV (Monitoring, Reporting, Verification) systems.
-
B. Structural and Technological Barriers
-
Limited R&D funding, fragmented policies.
-
Absence of region-specific biomass standards.
-
Low awareness among farmers, builders, local bodies.
-
No proven viable business models yet.
Roadmap for Large-scale Adoption
A. Policy & Market Interventions
-
Recognise biochar in Indian carbon market (to launch in 2026).
-
Integrate with:
-
Crop residue management schemes.
-
Bioenergy missions (rural and urban).
-
State Action Plans on Climate Change (SAPCCs).
-
B. Research and Standards
-
Invest in region-wise feedstock R&D.
-
Develop utilisation norms based on agro-climatic zones.
C. Employment and Economic Development
-
Village-level production units can generate 5.2 lakh rural jobs.
-
Create new income streams for farmers via carbon credits.
D. Public Awareness & Coordination
-
Cross-sectoral integration: Agriculture + Energy + Climate Policy.
-
National and state-level awareness programs on biochar use.
Conclusion
-
Biochar is not a silver bullet, but:
-
Offers a science-based, low-cost, and scalable solution for climate mitigation, agriculture improvement, waste management, and green construction.
-
With the right policy ecosystem, India can turn waste into wealth, and make biochar a key player in its net-zero journey and Sustainable Development Goals.
-
