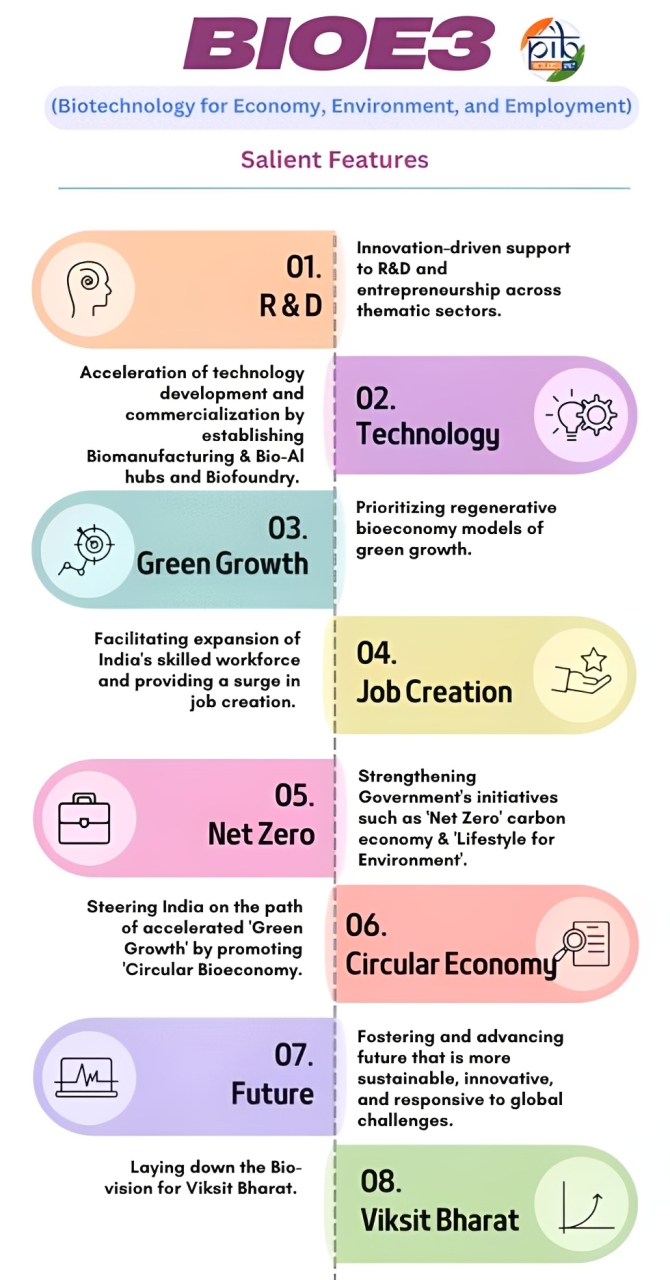
BioE3 Policy – Biotechnology for Economy, Environment and Employment
- Approval Date: 24 August 2024
- Approved by: Union Cabinet (proposal by Department of Biotechnology – DBT)
-
India’s first Biotechnology Policy focused on Fostering High Performance Biomanufacturing.
-
Lays the framework for the Biomanufacturing and Biofoundry Initiative.
-
Promote green growth by shifting from a consumptive manufacturing paradigm to regenerative, circular bioeconomy.
Rationale
-
Current unsustainable patterns: over-utilization of resources, waste generation, and high material consumption.
-
Consequences: climate change impacts — burning forests, melting glaciers, biodiversity loss.
-
Biomanufacturing Solution: Leverages living systems + engineering to produce commercially important bio-based products from biomass & waste resources.
Major Initiative Launched
Title: Fostering High Performance Biomanufacturing – An Integrated Approach towards Promoting Circular Economy for a Green, Clean & Prosperous India
Six Thematic Verticals of National Importance
-
Bio-based Chemicals & Enzymes – Sustainable industrial inputs replacing petrochemicals.
-
Functional Food & Smart Proteins – Nutraceuticals, alternative proteins for nutrition security.
-
Precision Biotherapeutics – Targeted therapies, personalised medicines, advanced biologics.
-
Climate Resilient Agriculture – Biotech-driven stress-resistant crops, sustainable farming inputs.
-
Biofuels & Carbon Capture – Next-gen bioenergy, CO₂ sequestration technologies.
-
Futuristic Marine & Space Research – Biotech applications in deep-sea & space environments.
Bio-Enablers (Infrastructure for Scaling)
-
Bio-AI Hubs: Artificial intelligence integration for biotech R&D.
-
Biofoundry/Biomanufacturing Hubs: Advanced facilities for design, prototyping, and scaling of biotech innovations.
Implementation Approach
-
National Consultation + Inter-ministerial coordination.
-
Public–Private Partnerships (PPP) for faster translation to market.
-
International collaboration to access frontier technologies.
Expected Impact
-
Green Growth through circular bioeconomy.
-
Surge in employment and entrepreneurial activity in biotech.
-
Acceleration towards Viksit Bharat@2047 bioeconomy targets.
-
Ethical governance: equitable access, biosafety, and ethical biotech practices.
- Bioeconomy: Uses renewable biological resources (land & sea – crops, forests, fish, animals, microbes) for food, products, textiles, and energy.
- Biotechnology: Integration of natural & engineering sciences to apply organisms, cells, and molecules for products/services.
-
Biomanufacturing: Uses engineered living systems to produce molecules/materials at scale.
-
Biofoundry:A biofoundry is a specialized, automated facility that accelerates biological research and product development by combining automation, artificial intelligence, and high-throughput experimentation. It essentially bridges the gap between design, engineering, and testing of biological systems, streamlining the "design-build-test-learn" cycle. Biofoundries enable faster, more efficient, and reproducible biological engineering for various applications, including pharmaceuticals, biofuels, and sustainable materials.
India’s Biotech Industry Status
-
Global Share: ~3% of global biotech.
-
GDP Share: ~2.6% (2021–22).
-
Start-ups: From 50 (2014) → 5,300 (2024) → expected 10,000+ by end of 2025.
-
Market Size: $10B (2014) → $80B (2023) → $300B (2030 target).
-
Goal: Top 5 global biomanufacturing hubs by 2025; fermentation capacity ↑ tenfold to 10M litres in 3–5 years.
