BioE3 Policy First Anniversary – ICGEB New Delhi Event (2025)
The Event (BioE3@1)
-
Occasion: First anniversary of the BioE3 Policy.
-
Host: International Centre for Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology (ICGEB), New Delhi.
-
Theme: “Institute–Industry Interaction for Climate Resilient Agriculture and Clean Energy”.
-
Collaborating Institutes:
-
National Agri Food Biotechnology Institute (NABI), Mohali
-
National Institute of Plant Genome Research (NIPGR), New Delhi
-
National Institute of Animal Biotechnology (NIAB), Hyderabad
-
Institute of Pesticide Formulation Technology (IPFT), Gurugram
-
Regional Centre for Biotechnology (RCB), Faridabad
Occasion: First anniversary of the BioE3 Policy.
Host: International Centre for Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology (ICGEB), New Delhi.
Theme: “Institute–Industry Interaction for Climate Resilient Agriculture and Clean Energy”.
Collaborating Institutes:
-
National Agri Food Biotechnology Institute (NABI), Mohali
-
National Institute of Plant Genome Research (NIPGR), New Delhi
-
National Institute of Animal Biotechnology (NIAB), Hyderabad
-
Institute of Pesticide Formulation Technology (IPFT), Gurugram
-
Regional Centre for Biotechnology (RCB), Faridabad
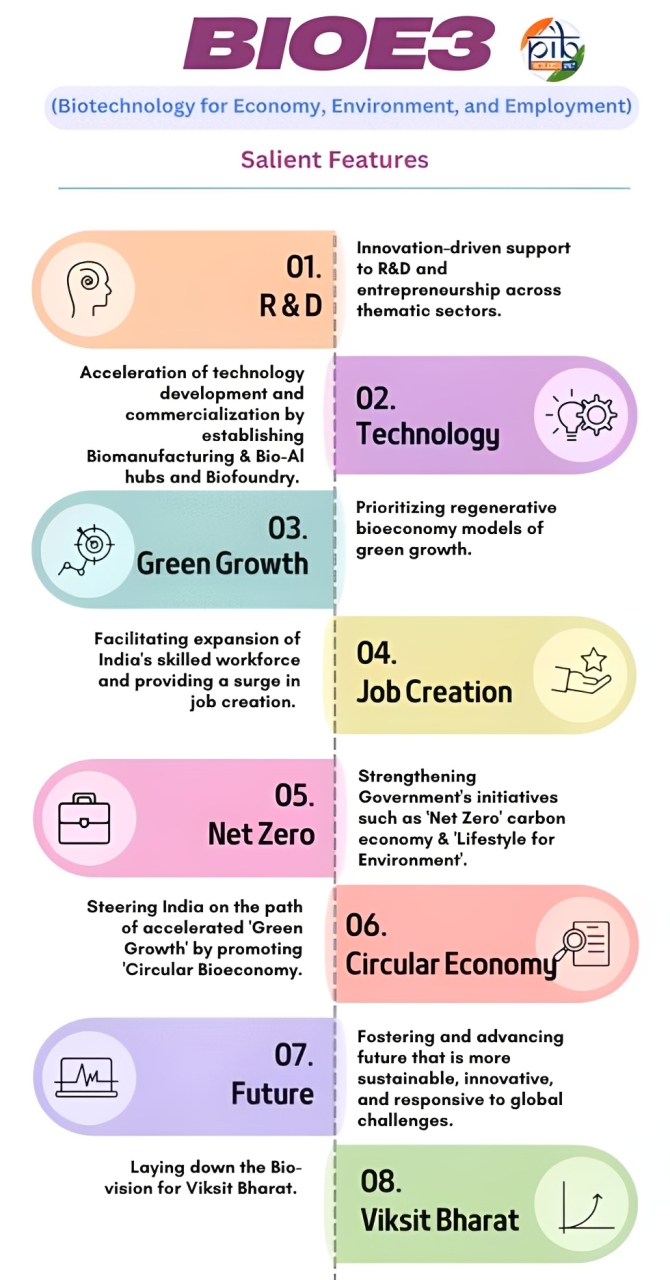
BioE3 Policy (Biotechnology for Economy, Environment & Employment)
Background
-
Approved by Union Cabinet: August 2024
-
Implements: Interim Budget 2024–25 scheme for Biomanufacturing & Biofoundry
-
Purpose: Integrate biotechnology with economy, environment, and employment to drive sustainable growth.
Approved by Union Cabinet: August 2024
Implements: Interim Budget 2024–25 scheme for Biomanufacturing & Biofoundry
Purpose: Integrate biotechnology with economy, environment, and employment to drive sustainable growth.
Objectives
-
Build a resilient biomanufacturing ecosystem in India.
-
Promote industrialization of biology for sustainability and circular economy.
-
Align biotechnology with Green Growth (Budget 2023–24), Lifestyle for Environment (LiFE), and Net Zero 2070 goals.
-
Foster R&D, entrepreneurship, and innovation in six thematic sectors.
Build a resilient biomanufacturing ecosystem in India.
Promote industrialization of biology for sustainability and circular economy.
Align biotechnology with Green Growth (Budget 2023–24), Lifestyle for Environment (LiFE), and Net Zero 2070 goals.
Foster R&D, entrepreneurship, and innovation in six thematic sectors.
Six Thematic Priority Sectors
-
Bio-based chemicals & enzymes
-
Functional foods & smart proteins
-
Precision biotherapeutics
-
Climate-resilient agriculture
-
Carbon capture & utilization
-
Futuristic marine & space research
Bio-based chemicals & enzymes
Functional foods & smart proteins
Precision biotherapeutics
Climate-resilient agriculture
Carbon capture & utilization
Futuristic marine & space research
Key Mechanisms
-
Biofoundries & Biomanufacturing Hubs
-
Operate on Design–Build–Test–Learn (DBTL) model.
-
Use AI, big data, synthetic biology, genetic engineering.
-
Enable scale-up and commercialization of bio-based products.
-
Example: ICGEB Biofoundry, New Delhi (20L capacity, bacteria & yeast platforms).
-
Bio-AI Hubs
-
Power data-driven predictive research.
-
Accelerate innovation in bio-based sectors.
Biofoundries & Biomanufacturing Hubs
-
Operate on Design–Build–Test–Learn (DBTL) model.
-
Use AI, big data, synthetic biology, genetic engineering.
-
Enable scale-up and commercialization of bio-based products.
-
Example: ICGEB Biofoundry, New Delhi (20L capacity, bacteria & yeast platforms).
Bio-AI Hubs
-
Power data-driven predictive research.
-
Accelerate innovation in bio-based sectors.
Space Research Component
-
Microalgae & Cyanobacteria Experiments on ISS
- Three indigenous robust microalgal species namely, Chlorella sorokiniana-I, Parachlorellakessleri-I and Dysmorphococcus globosus-HI, were experimented on the International Space Station (ISS) to study the impact of microgravity, CO2 and O2 levels simultaneously in space and on the Earth (indoor lab).
- In the second experiment, two cyanobacteria strains i.e., an Indian isolate of Spirulina, and a very fast-growing Synechococcus strain were also experimented for their growth on two different nitrogen sources nitrate and urea in the microgravity conditions provided by the ISS.
- Functions:
-
- Capture CO₂ in microgravity.
- Produce nutrients/food for astronauts.
- Demonstrate biological life support systems for future space missions.
Microalgae & Cyanobacteria Experiments on ISS
- Capture CO₂ in microgravity.
- Produce nutrients/food for astronauts.
- Demonstrate biological life support systems for future space missions.
India’s Bioeconomy Achievements (2014–2023)
-
Growth: $10 bn → $151 bn (ahead of 2025 target).
-
Share in GDP (2023): 4.25% of $3.55 trillion.
-
Biotech startups: 50 (2014) → 8,531 (2023).
-
Strong network via DBT–BIRAC support schemes.
Growth: $10 bn → $151 bn (ahead of 2025 target).
Share in GDP (2023): 4.25% of $3.55 trillion.
Biotech startups: 50 (2014) → 8,531 (2023).
Strong network via DBT–BIRAC support schemes.
International Centre for Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology (ICGEB)
Established as a project of the United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO) in 1983 became an independent international organisation in 1994.
-
Headquarters & Labs:
-
HQ: Trieste, Italy
-
New Delhi, India
-
Cape Town, South Africa
-
-
Members: Over 65 countries are part of it.
-
Staff: 600+ scientists and professionals.
-
Budget: Around €60 million (as of 2023).
Focus Areas
-
Research in infectious and non-communicable diseases, plant biology, industrial and medical biotechnology.
-
Education & Training: PhD and postdoctoral fellowships, workshops, and scientific meetings.
-
Grants & Funding: Provides competitive grants to scientists in member countries.
-
Technology Transfer: Helps move scientific innovations from labs to industry.
Significance
-
Acts as a global hub for biotechnology research and training.
-
Promotes international collaboration, especially supporting developing countries in biotech capacity-building.
-
Strengthens the link between science, innovation, and industry for solving global health, agriculture, and environmental challenges.
Biomanufacturing
-
Definition: The use of biological systems (like microbes, enzymes, cells) to produce industrially useful products.
-
Goal: Replace fossil fuel–based processes with bio-based, sustainable methods.
-
Products: Food supplements, smart proteins, bioplastics, biofuels, drugs, enzymes, bio-chemicals.
Example: Producing insulin using genetically modified bacteria instead of chemical synthesis.
Biofoundry
-
Definition: A specialized infrastructure facility where biomanufacturing research is done systematically using an engineering approach.
-
Principle: Works on DBTL cycle (Design → Build → Test → Learn).
-
Design: Uses AI, bioinformatics, and big data to design DNA sequences and pathways.
-
Build: DNA assembly, transformation of microbes.
-
Test: Screening products and optimizing processes.
-
Learn: Machine learning to improve results.
-
Example: The ICGEB Biofoundry, New Delhi, which works on bacteria and yeast for products in food, chemicals, drugs, and energy.
Difference Between the Two
-
Biomanufacturing = The process of making bio-based products.
-
Biofoundry = The facility where systematic design, testing, and scaling of those processes happen.
