Blue-Green Ammonia: Cheaper and Greener
Background
Ammonia is vital for fertilisers, shipping fuel, and energy storage, but conventional production (via Haber–Bosch using natural gas) is carbon-intensive, contributing ~1.8% of global CO₂ emissions.
Alternatives:
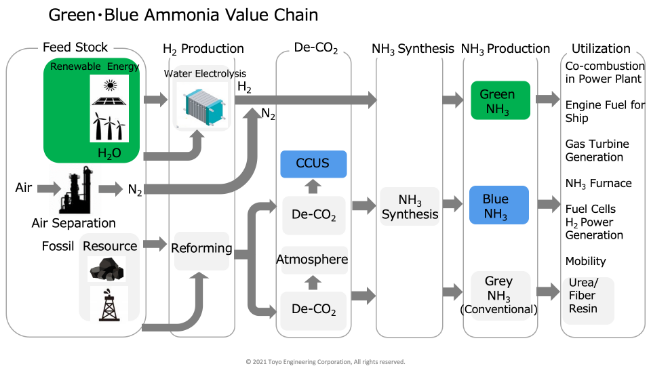
Blue Ammonia → From natural gas + carbon capture & storage (CCS).
Green Ammonia → From renewable-powered electrolysis of water to produce hydrogen.
The Hybrid Pathway: Blue-Green Ammonia
A recent study in Energy & Fuels proposes a combined pathway:
Uses oxygen from electrolysis in the natural gas reforming step.
Uses air for nitrogen supply.
Benefits:
7% lower levelised cost of ammonia (LCOA) compared to standalone plants.
63% reduction in lifecycle GHG emissions.
More efficient integration of carbon capture + renewables.
Significance
Decarbonising Fertiliser Sector – India, one of the largest consumers of urea/ammonia-based fertilisers, could cut emissions and import bills.
Energy Transition – Blue-green ammonia could become a low-carbon fuel for shipping and hydrogen economy.
Cost Competitiveness – Hybrid route reduces dependency on expensive renewable-only (green) hydrogen.
Strategic Fit for India –
National Green Hydrogen Mission (2023) targets 5 MMT hydrogen production by 2030.
India exploring ammonia as hydrogen carrier for export markets (Japan, EU).
This hybrid pathway may help bridge the transition until renewables scale up fully.
Challenges
CCS infrastructure in India is limited.
High capital investment for electrolysers.
Policy and pricing frameworks needed for carbon markets & incentives.
Way Forward
Integrate blue-green ammonia in India’s Green Hydrogen & Fertiliser missions.
Promote R&D in hybrid ammonia plants with industry-academia collaboration.
Develop carbon capture hubs linked to fertiliser and refinery clusters.
Explore exports of low-carbon ammonia to tap global clean energy demand.
