BNHS vulture release programme
The Bombay Natural History Society (BNHS) has bred over 800 vultures at its conservation breeding centres in India.
BNHS will release six vultures (three male + three female; slender-billed and white-rumped species) in January 2026.
Age of released vultures: 2–3 years.
Release sites: Kamrup and Biswanath districts, Assam.
These birds were bred at the BNHS Vulture Conservation Breeding Centre in Rani (Kamrup district).
Why Kamrup and Biswanath?
Both districts lie within the natural range of these vulture species.
Existing wild flocks already present.
Biswanath is close to Kaziranga National Park, offering a suitable habitat.
Biological features of vultures
Live in flocks.
Attain sexual maturity at ~5 years.
Lifespan: 50 to 60 years.
High immunity; low susceptibility to infections.
Founder stock for this programme was collected from various parts of Assam.
Species distribution
Slender-billed vulture: mainly found in Assam.
White-rumped vulture: found across India.
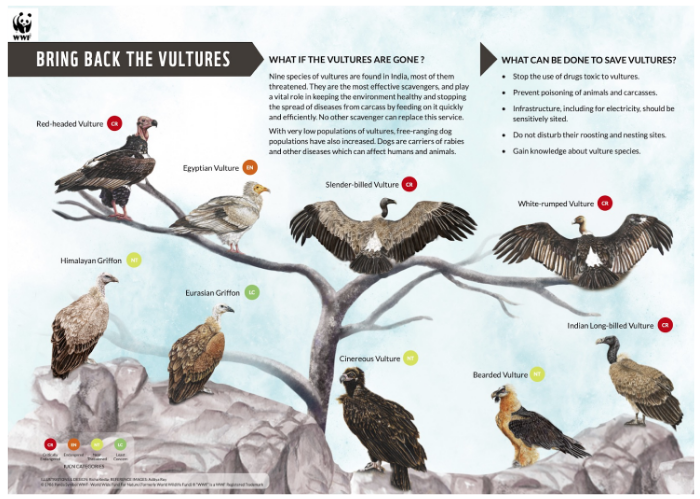
India’s vulture population and status
Total vultures in India: around 20,000, across nine species, including bearded vulture, griffon vulture, cinereous vulture.
Critically Endangered (CR)
IUCN:
White-rumped vulture (Gyps bengalensis) – Critically Endangered
Slender-billed vulture (Gyps tenuirostris) – Critically Endangered
Long-billed vulture (Gyps indicus) – Critically Endangered
Red-headed vulture (Sarcogyps calvus) – Critically Endangered
Endangered (EN)
IUCN recognises the following as Endangered:
Egyptian vulture (Neophron percnopterus) – Endangered
Himalayan griffon vulture (Gyps himalayensis) – Near Threatened (NT)* globally but considered Endangered in India-specific conservation assessments and by Indian agencies due to regional decline.
Prelims Practice MCQs
Q. Which of the following species is correctly matched with its IUCN status?
a) Red-headed vulture – Endangered
b) Slender-billed vulture – Critically endangered
c) Himalayan griffon – Vulnerable
d) White-rumped vulture – Near threatened
Correct answer: b
Explanation:
Slender-billed vulture is critically endangered. Red-headed and white-rumped vultures are also critically endangered; Himalayan griffon is endangered, not vulnerable.
Q. Which of the following statements regarding the slender-billed vulture is correct?
a) It is primarily distributed in southern India and Sri Lanka.
b) It is an Old World vulture native to sub-Himalayan regions and Southeast Asia.
c) It is found only in the Tibetan plateau.
d) It is widely distributed across Europe and West Asia.
Correct answer: b
Explanation:
The slender-billed vulture (Gyps tenuirostris) is native to sub-Himalayan regions and Southeast Asia, with its strongest presence in Assam today.
Egyptian vulture - southern Europe and North Africa to central Asia and the Indian subcontinent
The White-rumped vulture's range includes Pakistan, India, Bangladesh, Nepal, Bhutan, and parts of Southeast Asia, specifically Myanmar, Laos, Cambodia, and southern Vietnam
The slender-billed vulture (Gyps tenuirostris) is an Old World vulture species native to sub-Himalayan regions and Southeast Asia. (mainly found in assam )
