Bonnet Macaques
Kerala Forest Department to seek approval from the Union Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change.
-
Bonnet macaques are listed under Schedule I of the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972 – requiring central permission.
-
The initiative is part of “Mission Bonnet Macaque”, a 10-point programme to mitigate conflict.
-
The plan involves capturing, sterilising, monitoring health, and releasing the monkeys back into their original habitats.
-
Culling not considered—unlike wild pigs, which are currently culled in the state.
-
Additional measures include waste management in eco-tourism zones to reduce monkey access to food waste.
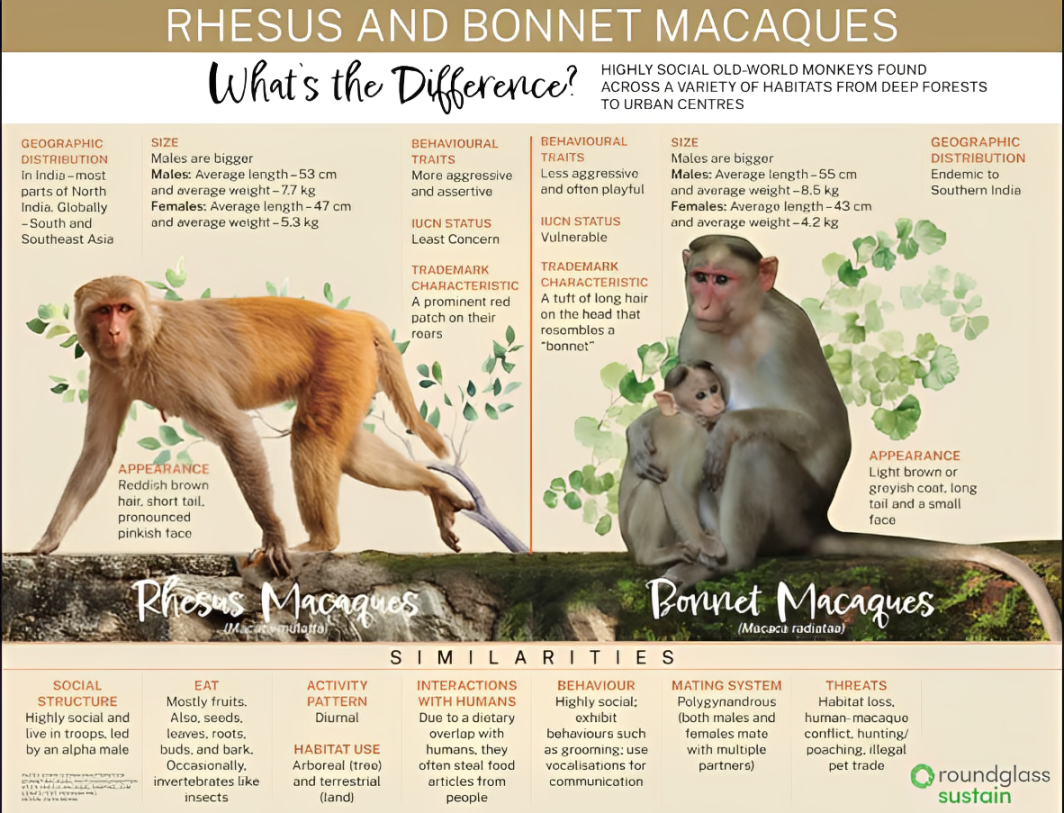
Bonnet Macaque – :
-
Scientific Name: Macaca radiata
-
Common Name: Bonnet macaque
-
Habitat: Endemic to South India; found in forests, villages, urban areas
-
Behavior: Highly social, forms troops, adapts to human presence
-
Threats:
-
Habitat loss and fragmentation
-
Urbanisation
-
Road accidents
-
Human-animal conflict
-
-
IUCN Red List Status: Vulnerable
-
Due to population decline and increasing threats
-
-
Legal Protection in India: Schedule I, Wildlife Protection Act, 1972 (highest protection level)
Endemic Region: Southern India
-
Bounded by the Indian Ocean on three sides
-
Godavari and Tapti Rivers and competition with rhesus macaque restrict northern spread
Habitat Shift: Land use changes have altered its traditional range, increasing overlap with rhesus macaque—raising conservation concerns
Behavior and Ecology:
-
Activity: Diurnal (active during the day), both arboreal (tree-dwelling) and terrestrial (ground-dwelling)
-
Diet: Omnivorous
-
Eats fruits, seeds, nuts, flowers, invertebrates, cereals
-
Frequently raids crops and homes; feeds on food provided by humans (commensal behavior)
-
Social Behavior:
-
Affiliative Gesture:
-
Lip-smacking: Common friendly gesture involving rapid mouth movements with audible sound
-
-
Fear/Submissive Gesture:
-
Grimace: Shown by subordinates during aggressive encounters
-
Social Structure:
-
Hierarchy:
-
Follows a linear dominance hierarchy
-
Alpha, beta, gamma males ranked in decreasing dominance
-
Females have a separate, stable hierarchy
-
Males are dominant over females; their hierarchy is dynamic and involves frequent competition
-
-
Group Dynamics:
-
Females stay in their natal group(where they were born)
-
Males disperse to other groups upon maturity
-
-
These combined efforts aim to ensure population control without endangering the species, balancing conservation and community welfare.
