BRICS - 2025 Brazil Summit
What Is BRICS?
-
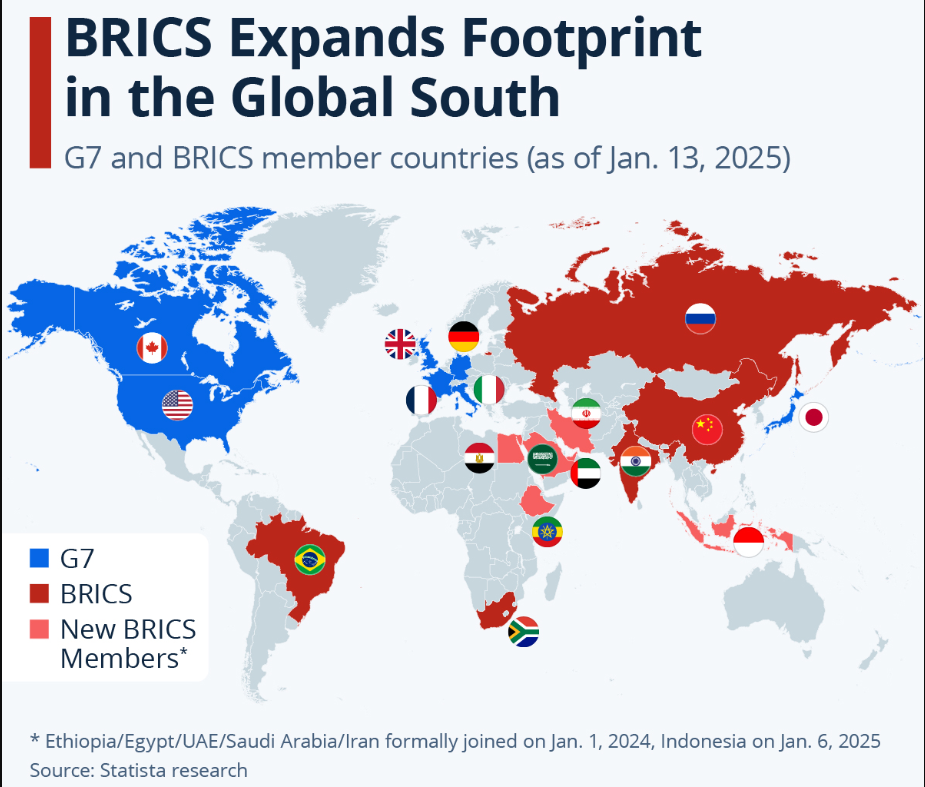
BRICS is an informal bloc of emerging economies: Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa, now expanded to 11 members.
-
Originally coined as "BRIC" by economist Jim O’Neill (2001), institutionalized with the first summit in 2009.
-
South Africa joined in 2010.
-
BRICS aims to provide a counterweight to Western influence, especially in the World Bank, IMF, UN Security Council, and G7.
Why Is BRICS Expanding?
-
Seeks to represent the Global South and reform global governance.
-
Expansion aims to increase economic heft and geopolitical influence.
-
Recent members include:
-
2023: Egypt, Ethiopia, Iran, Saudi Arabia, UAE (Argentina declined).
-
2024: Indonesia joined;
"Partner Country" status introduced for Belarus, Bolivia, Cuba, Kazakhstan, Malaysia, Nigeria, Thailand, Uganda, Uzbekistan.
-
-
Over 30 countries applied to join BRICS in 2024.
Geopolitical Significance of Expansion
-
BRICS now accounts for:
-
>25% of global GDP
-
~45% of global population
-
-
Influence in global conflicts (Ukraine, Gaza), energy markets (Saudi & UAE), and de-dollarization efforts.
-
Challenges:
-
Internal rivalries: India-China, Saudi-Iran, Egypt-Ethiopia.
-
Governance and decision-making complexities.
-
Uneven relations with the West.
-
Institutions Established by BRICS
-
New Development Bank (NDB):
-
Headquartered in Shanghai, operational since 2016.
-
Offers loans, guarantees, equity to sustainable development & infrastructure.
-
Approved $32+ billion across 96 projects.
-
Focus on clean energy, transport, sanitation.
-
New regional offices in Brazil, India, South Africa, Russia.
-
Opened membership to non-BRICS developing countries in 2021.
-
-
Contingent Reserve Arrangement (CRA):
-
A currency stabilization fund among BRICS central banks.
-
Functions like a mini-IMF during currency liquidity crises.
-
Limited to original BRICS countries.
-
Key Issues & Internal Challenges
-
Russia’s invasion of Ukraine: ICC warrant complicates Putin's participation.
-
China-India border disputes: Hinders bloc unity.
-
Economic slowdowns in China, Brazil, South Africa.
-
Authoritarian vs democratic divides: Iran, Russia vs India, Brazil.
De-Dollarization & Currency Initiatives
-
BRICS countries advocate for:
-
Reduced dependence on USD.
-
Increased trade in local currencies (like CNY, INR).
-
Proposal for a common BRICS currency (Lula da Silva).
-
Ideas of crypto or currency basket, but feasibility is questionable due to:
-
Macroeconomic divergence.
-
Lack of fiscal union.
-
Dominance of USD in 80%+ of global trade.
-
-
Western Response
-
US and EU downplay BRICS as a geopolitical rival.
-
Biden: BRICS not seen as a major threat.
-
Trump (2025): Called BRICS "dead", threatened 100% tariffs if de-dollarization proceeds.
-
EU analysts warn that Global South discontent is growing due to lack of real reform in Bretton Woods institutions.
What’s Next? – 2025 Rio Summit
-
Brazil chairs BRICS in 2025.
-
Focus areas:
-
Reform of global governance systems.
-
Enhancing South-South cooperation.
-
-
Notable absentees:
-
For the first time China's Xi Jinping is absent (schedule conflict).
-
Russia’s Putin (ICC arrest warrant).
-
-
Prospective new members: Azerbaijan, Turkey, Malaysia, etc.
