Catastrophe Bonds (Cat Bonds)
-
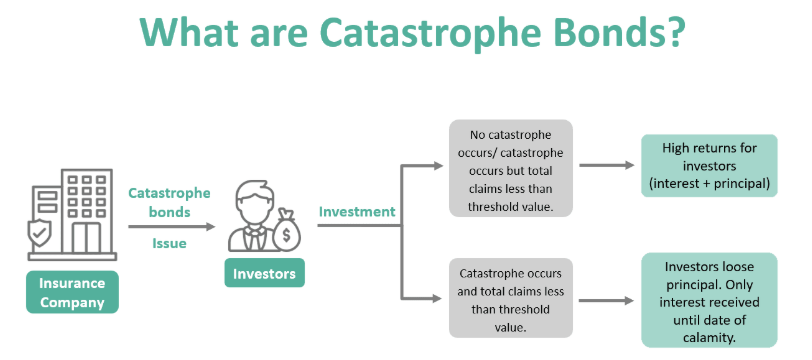
Catastrophe Bonds (Cat Bonds) are insurance-cum-debt instruments that transfer disaster risk from governments to global investors by securitising risk, enabling faster payouts and reducing reliance on traditional insurers.
-
How They Work:
-
Issued by: Sovereign governments (sponsors) via intermediaries like the World Bank or reinsurers.
-
Investors receive high returns (coupon rates) but risk losing principal if a disaster occurs.
-
Payouts are trigger-based, often linked to disaster magnitude thresholds.
-
-
Investor Attraction:
-
Disasters (earthquakes, cyclones) are uncorrelated with financial markets, providing portfolio diversification.
-
Main investors: Pension funds, hedge funds, family offices.
-
Global issuance: $180 billion to date, $50 billion currently outstanding.
-
-
India’s Context:
-
India has low disaster insurance coverage, making the population vulnerable to loss.
-
Rising climate risks (cyclones, floods, earthquakes) make post-disaster funding burdensome.
-
India has already allocated $1.8 billion/year since FY21-22 for disaster mitigation.
-
-
Proposal for South Asia:
-
India could be a lead sponsor of a South Asian Cat Bond to pool regional risks.
-
Shared coverage for hazards like earthquakes in Nepal, Bhutan, India, or cyclones/tsunamis in Bay of Bengal countries.
-
Risk pooling would lower premiums and increase regional resilience.
-
-
Limitations:
-
Trigger design flaws (e.g., no payout if a disaster falls just below threshold).
-
No disaster = no payout, which may be seen as wasteful spending.
-
Transparent comparison between premium costs and historical relief expenditure is essential before adoption.
-
Cat bonds can offer India and South Asia an innovative, cost-effective, and timely financial tool for disaster resilience, but careful design and risk assessment are critical to ensure effectiveness.
