East Timor Joins ASEAN 2025
Background
Event: The Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) officially welcomed East Timor (Timor-Leste) as its newest member.
Occasion: ASEAN Summit, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia (October 2025).
Significance: East Timor’s inclusion expands ASEAN to 11 member countries.
PM Narendra Modi welcomed East Timor during the summit.
About East Timor (Timor-Leste)
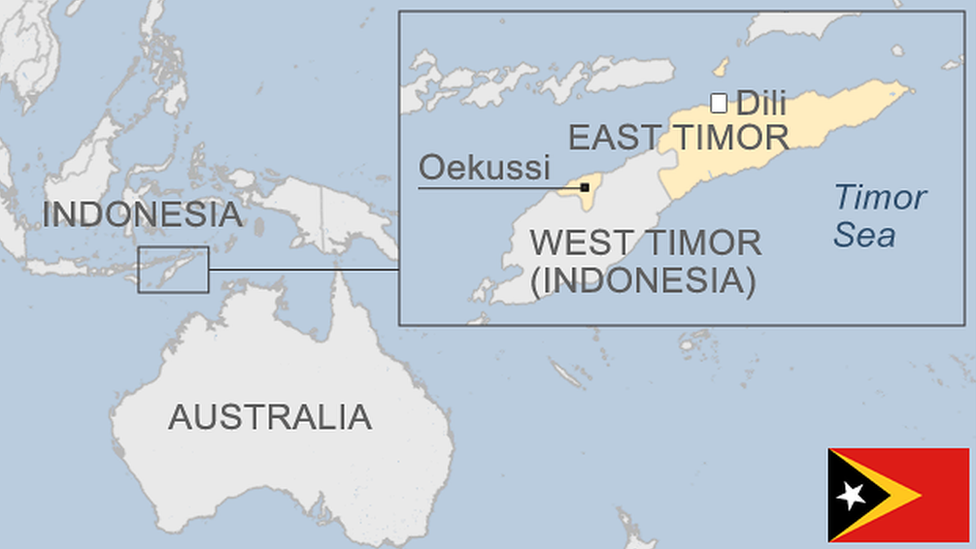
Location: Island nation in the Pacific Ocean, north of Australia.
Population: ~1.4 million.
Colonial Past:
Portuguese colony for over four centuries.
Declared independence in 1975, but invaded by Indonesia soon after.
After prolonged resistance and UN supervision, gained full independence in 2002.
Current President: Jose Ramos-Horta, Nobel Peace Prize Laureate (1996) for peace efforts.
Historical Context
Indonesian Occupation (1975–1999):
Violent annexation following declaration of independence.
Thousands killed; large-scale human rights violations.
Ended after UN-supervised referendum (1999) led to independence transition.
Global Involvement:
Henry Kissinger (US) and President Suharto (Indonesia) had discussed the invasion’s geopolitical implications during the Cold War.
East Timor’s struggle was viewed through anti-communist and regional strategic lenses.
ASEAN and East Timor
ASEAN Founded: 1967, with original members Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand signed the ASEAN Declaration at Saranrom Palace in Bangkok. (Trick: IMPST)
Current (Now 11) Members:
Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam, and East Timor.ASEAN GDP: around $3.8 trillion.
Key Agreements: Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP).
Economic & Social Aspects of East Timor
Poverty: Around 42% live below the national poverty line.
Demography: Nearly two-thirds of citizens are under 30 years old.
Economy:
Largely dependent on oil and gas revenue.
Needs diversification into agriculture, fisheries, and services.
Challenges:
Limited capacity and infrastructure.
Elite aware of economic burdens; cautious about integration pace.
President Ramos-Horta stated that capacity-building will be a long-term process.
Significance of ASEAN Membership
Political: Enhances regional legitimacy and security cooperation.
Economic: Access to ASEAN’s trade agreements and development programs.
Strategic: Provides counterbalance to Chinese influence in maritime Southeast Asia.
Symbolic: Marks East Timor’s transition from a post-conflict state to a regional partner.
Trick to remember
Founding Members (1967) → “IM-PST”
👉 I M P S T
I – Indonesia
M – Malaysia
P – Philippines
S – Singapore
T – Thailand
Later Members (Joined after 1967)
B – Brunei (joined 1984)
V – Vietnam (joined 1995)
L – Laos (joined 1997)
M – Myanmar (joined 1997)
C – Cambodia (joined 1999)
E – East Timor (2025)
Prelims Practice MCQ
Q. Consider the following statements about the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN):
ASEAN was established in 1967 with five founding members.
India is a founding member of ASEAN.
After East Timor’s inclusion, ASEAN now has 11 members.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 3 only
B. 1 and 2 only
C. 2 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
✅ Answer: A
Explanation: India is not a member of ASEAN; statement 2 is incorrect.
Q. With reference to East Timor (Timor-Leste), consider the following statements:
It was a Portuguese colony that was later occupied by Indonesia.
It gained full independence after a United Nations-supervised referendum.
Jose Ramos-Horta, its current President, is a Nobel Peace Prize laureate.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1, 2 and 3
D. 1 only
✅ Answer: C
Explanation: All statements are correct. East Timor’s colonial and independence trajectory matches all three.
