Electronics Component Manufacturing Scheme (ECMS)

Context
The Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) has approved 22 additional projects under the Electronics Component Manufacturing Scheme (ECMS).
Total scheme outlay: ₹22,919 crore.
Approved investment (latest tranche): ₹41,863 crore.
Objectives of ECMS
Strengthen domestic manufacturing of electronic components.
Reduce import dependence, especially on East Asian supply chains.
Promote employment generation and value addition in India.
Complement India’s electronics manufacturing ecosystem alongside PLI schemes.
Incentive Structure
Incentives are linked to:
Incremental production
Employment generation
Performance-based payouts, not upfront subsidies.
Incentives will be given to firms that achieve production milestones fastest → “first-to-finish” approach.
Beneficiary
Covers:
Small and medium Indian firms
Large established players, including Tata Electronics Pvt. Ltd.
Indicates an inclusive industrial policy rather than one focused only on large conglomerates.
Electronics Component Manufacturing Scheme (ECMS)
Scope and coverage
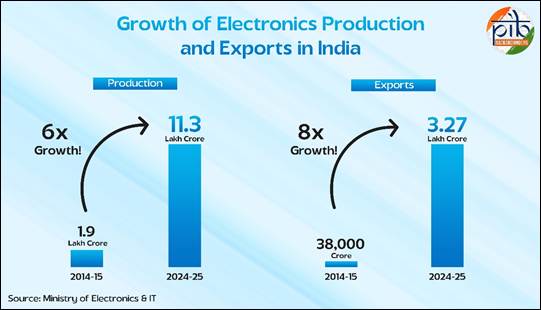
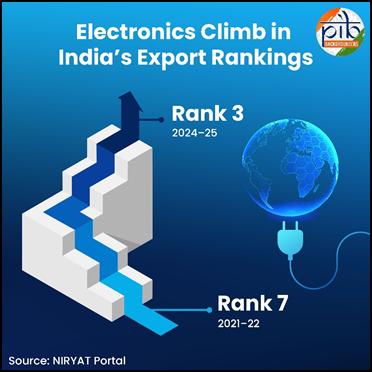
Electronics sector: India’s export and production transformation Export performance
 Production growth
| ||
Prelims Practice MCQs
Q. Consider the following statements regarding the Electronics Component Manufacturing Scheme (ECMS):
It provides incentives based on incremental production and employment.
The incentives are given as upfront capital subsidies.
The scheme encourages faster completion of production milestones.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1 and 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Correct Answer: (b)
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct – incentives are performance-linked.
Statement 2 is incorrect – payouts are not upfront subsidies.
Statement 3 is correct – incentives favour firms that reach targets early.
Q. With reference to India’s electronics manufacturing policies, consider the following:
ECMS focuses primarily on finished electronic goods.
ECMS aims to reduce India’s dependence on imported electronic components.
The scheme includes both MSMEs and large firms.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Correct Answer: (b)
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect – ECMS focuses on components, not finished goods.
Statement 2 is correct – import substitution is a core goal.
Statement 3 is correct – both small firms and large players are covered.