Golden Dome & Its Legal and Geopolitical Implications
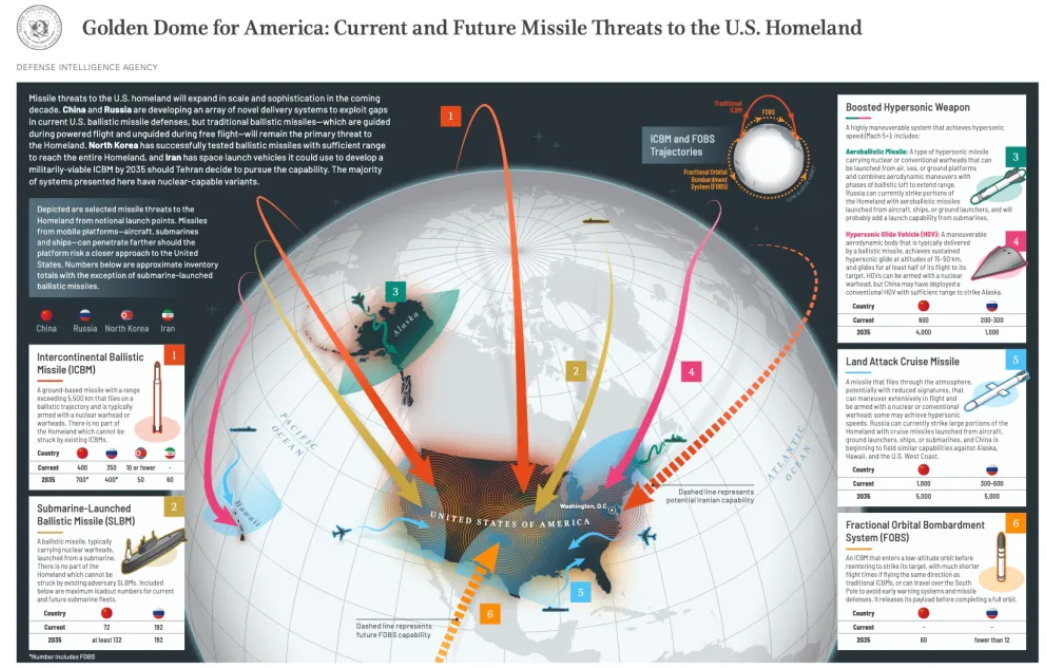
1. What is the Golden Dome?
-
A proposed $175 billion U.S. space-based missile shield, announced by President Trump in May 2025.
-
Aims to counter ballistic, hypersonic, and orbital threats.
-
Involves a constellation of satellite interceptors, possibly armed with kinetic or directed-energy weapons.
2. Legal Concerns under International Space Law
-
Outer Space Treaty (OST), 1967 – Article IV:
-
Prohibits placement of nuclear or WMDs in orbit.
-
Bans military activities on celestial bodies.
-
Allows peaceful use and scientific military presence.
-
-
Loophole: Treaty doesn’t explicitly ban conventional weapons in space.
-
Risk: Although not legally violating OST, the strategic impact (first-strike advantage, destabilisation) contravenes the spirit of arms control.
3. Threat to Global Norms
-
Violates UN’s PAROS (Prevention of Arms Race in Outer Space) norm.
-
Dual-use ambiguity:
-
Interceptors meant for missile defence could target satellites.
-
Risks mistrust, miscalculation, and strategic instability.
-
-
China & Russia have condemned the move.
4. India’s Strategic Dilemma
-
India is a partner in space situational awareness with the U.S.
-
Faces a conflict:
-
Tactical alignment with U.S.
-
But a normative commitment to peaceful use of space.
-
-
Risks:
-
Association may undermine India’s leadership in Global South & PAROS advocacy.
-
May affect India’s credibility in space governance debates.
-
5. Implications for India’s Space Activities Bill
-
The bill is expected to regulate dual-use platforms, private participation, and international obligations.
-
Golden Dome challenges India to:
-
Define clear boundaries between cooperation and militarisation.
-
Uphold normative leadership without hurting strategic ties.
-
6. Wider Global Repercussions
-
Golden Dome could:
-
Normalize weaponisation of space.
-
Trigger arms races, leading to space becoming a battlefield.
-
Force smaller nations to adopt asymmetric warfare (cyberattacks, jamming, debris generation).
-
-
Could unravel 58 years of peaceful space cooperation under OST.
7. Way Forward
-
Modernise international space law, especially OST’s provisions on conventional weapons and dual-use technologies.
-
India and others must advocate:
-
Binding treaties banning all types of space-based weapons.
-
Transparency and confidence-building measures in space military activities.
-
-
National laws like India’s Space Activities Bill should:
-
Set clear defence cooperation guidelines.
-
Promote responsible space practices.
UPSC Syllabus
GS Paper 2 – International Relations
-
Bilateral ties (India-U.S. strategic partnership)
-
Role of international institutions and treaties (OST, PAROS)
-
Global governance of commons (Outer Space)
GS Paper 3 – Security and Technology
-
Strategic implications of space weaponisation
-
Dual-use technology and arms race in outer space
-
Cybersecurity, satellite defence, and AI in military domain
Essay & Ethics
-
Ethical challenges in militarising commons like space
-
Balancing technological progress with international peace
