How is Global Shipping Trying to Decarbonise?
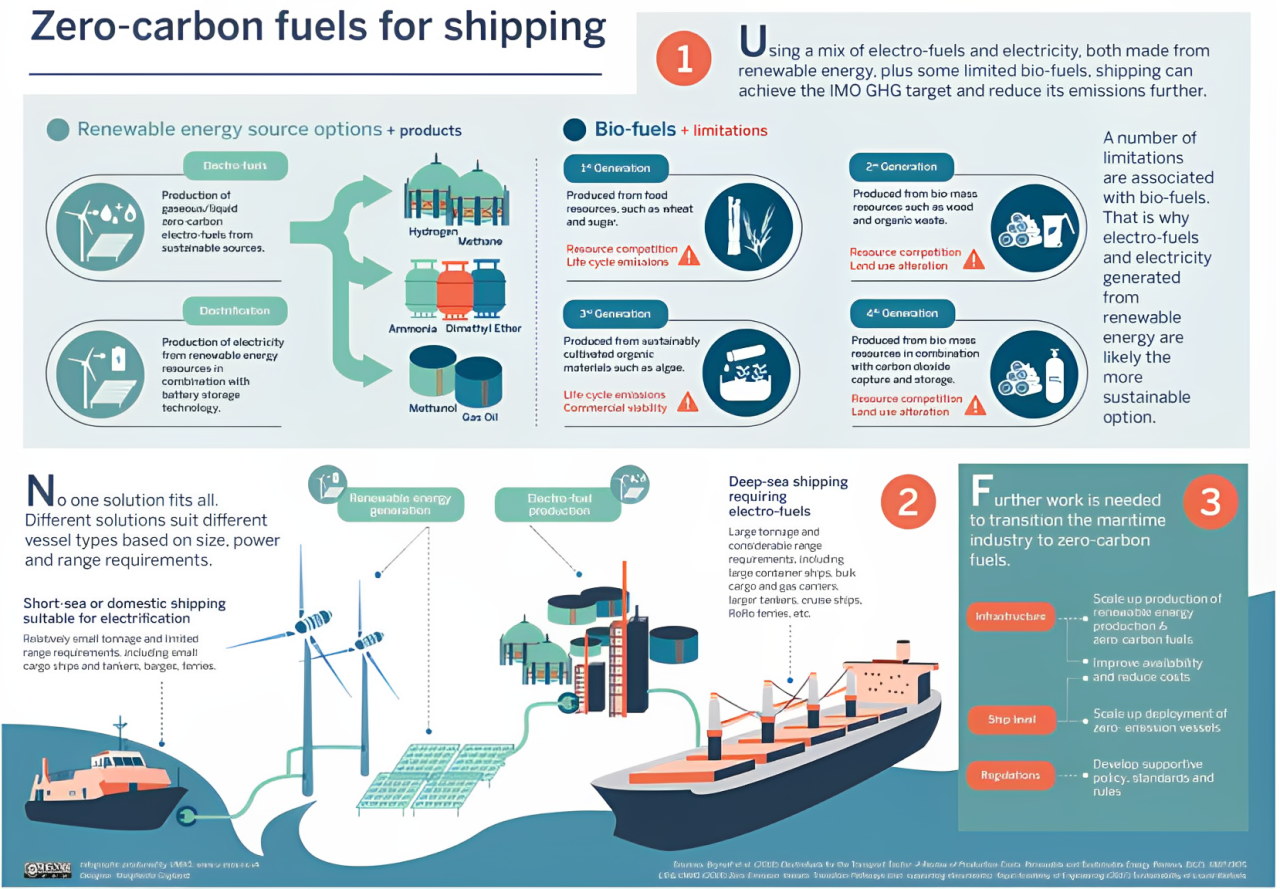
Context:
Global shipping aims to achieve decarbonisation by 2040–2050. This is both a climate imperative and a strategic opportunity for India to become a green fuel hub.
1. Current and Future Fuels in Shipping
-
Present fuels: Very Low Sulphur Fuel Oil (VLSFO), diesel, LNG (methane-based fuel).
-
Transition fuels: LNG, due to higher efficiency.
-
Green fuels for the future:
-
Green Methanol: Made from green hydrogen and CO₂; emits 10% of CO₂ compared to conventional fuels. Easy to store and use.
-
Green Ammonia: Made from green hydrogen and nitrogen; emits no GHGs, but harder to handle onboard.
-
Biofuels and e-methanol also in use.
-
2. Production of Green Fuels
-
Green hydrogen: Produced via electrolysis of water using renewable energy.
-
Green ammonia: Stable and preferred over hydrogen for shipping and fertilizer needs.
-
Green methanol: Easier storage and compatible with current engine tech but expensive due to high energy input (10–11 MWh/tonne).
3. Shipping Industry Trends
-
Methanol engines gaining traction (360+ ships on order/operational).
-
Major companies like Maersk, CMA CGM, and Evergreen investing in methanol ships.
-
Price gap remains: Green methanol is ~$1,950/tonne vs. VLSFO at ~$560/tonne (Feb 2025).
4. India’s Decarbonisation Strategy
-
Committed to decarbonising domestic shipping.
-
Developing green fuel bunkering hubs (e.g., Tuticorin, Kandla).
-
Aiming to export green fuels to hubs like Singapore, which accounts for ~25% of global ship fuelling.
5. Enabling India’s Green Fuel Economy
-
Challenges: Need for imported solar panels, electrolysers, and high upfront costs.
-
Opportunities:
-
Use sovereign guarantees, PLI schemes, and CCUS incentives to attract investment.
-
Build domestic electrolyser manufacturing (target: 1.5 GW capacity).
-
Leverage solar energy growth model (from 2.82 GW in 2014 to 105 GW in 2025).
-
6. Rebooting Indian Shipbuilding
-
Government has pledged $10 billion to purchase 110 ships.
-
Aim to make 10–20% of them green fuel-capable, Indian-built, and Indian-flagged.
-
Seeking foreign partnerships (e.g., South Korea, Japan) to enhance shipbuilding capacity.
-
Retrofitting existing ships and building new ones to support green fuel use.
