Immunology and the Future of Biomedicine
Introduction
Immunology — once an abstract science — is now central to modern medicine.
It influences public health, vaccine development, cancer therapy, and autoimmune disease treatment.
The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted immunology as a pillar of national and global health security.
Historical Background
Edward Jenner (1796): Discovered the principle of vaccination using cowpox to prevent smallpox — before immunology was formally conceptualised.
Formalisation: The field matured in the 20th century with advances in cell biology and molecular genetics.
Nobel Legacy:
Immunology has received 16 Nobel Prizes with 31 laureates, including 21 in the last 50 years.
This demonstrates its transformative contribution to biomedical science.
Nobel Prize 2025 – Peripheral Immune Tolerance
Laureates: Mary E. Brunkow, Fred Ramsdell, and Shimon Sakaguchi.
Discovery: Identified Regulatory T Cells (Tregs) responsible for peripheral immune tolerance.
Significance:
Prevents autoimmune attacks.
Opens avenues for treating autoimmune diseases, cancers, and organ transplant rejection.
Reinforces immunology’s centrality in understanding immune balance.
Immunology During COVID-19
The pandemic was a turning point for immunological innovation.
mRNA vaccine technology, awarded the Nobel Prize 2023, emerged from decades of immunology research.
Demonstrated how translational immunology can shape global public health, economy, and resilience.
Also underlined the importance of preparedness and robust research ecosystems.
Expanding Scope of Immunology
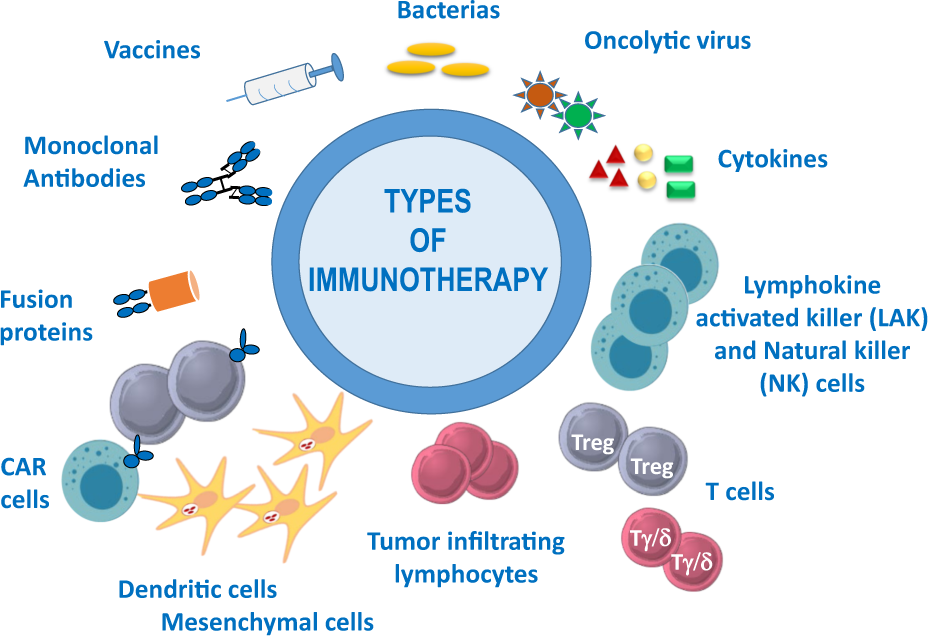
Cancer Immunotherapy
Checkpoint inhibitors (2018 Nobel Prize), CAR-T cell therapy, and cancer vaccines are reshaping oncology.
Immune-based treatments now complement chemotherapy and radiation.
Neuroimmunology
Research linking inflammation with depression, Alzheimer’s, and Parkinson’s.
Opens therapeutic pathways for neurodegenerative and psychiatric disorders.
Metabolic and Ageing Research
Immune mechanisms affect metabolic regulation and ageing processes.
Prospect of immune-modulating drugs for diabetes, obesity, and longevity.
Inference:
The immune system acts as a master regulatory network, not merely a defense system.
Strategic Importance for India
India faces a dual burden of communicable and non-communicable diseases.
Investing in immunology education, research, and translational medicine is critical.
Offers opportunities to:
Develop region-specific vaccines.
Study population-based immune variations.
Create affordable immunotherapies for Indian patients.
Strengthening India’s Immunological Base
Educational Reform
Introduce stronger immunology curricula at undergraduate and postgraduate levels.
Encourage interdisciplinary collaboration between lab researchers and clinicians.
Research Ecosystem
Support public funding for immunology-focused projects.
Build centres of excellence in immunological and translational research.
Policy and Collaboration
Promote international partnerships and biotech innovation ecosystems.
Link immunology with Ayush and traditional systems for integrated approaches.
Way Forward
Nations that invest in immunological education and infrastructure will lead the next biomedical revolution.
For India:
Immunology offers a path from being a provider of healthcare to becoming a leader in medical innovation.
The goal is to ensure that the benefits of modern immunology reach all citizens — achieving both equity and excellence.
Prelims Practice MCQ
Q. Checkpoint inhibitors, CAR-T cell therapies, and cancer vaccines are examples of:
A) Chemotherapy-based treatments
B) Immunotherapies that harness the immune system against tumors
C) Hormone regulation therapies
D) Gene silencing techniquesAnswer: B
