Kunar River
Context
The Taliban government in Afghanistan announced plans to construct a series of dams on the Kunar River.
The move is seen as an assertion of Afghanistan’s “water sovereignty” and could have significant geopolitical and environmental implications for Pakistan.
Key Points
Kunar River:
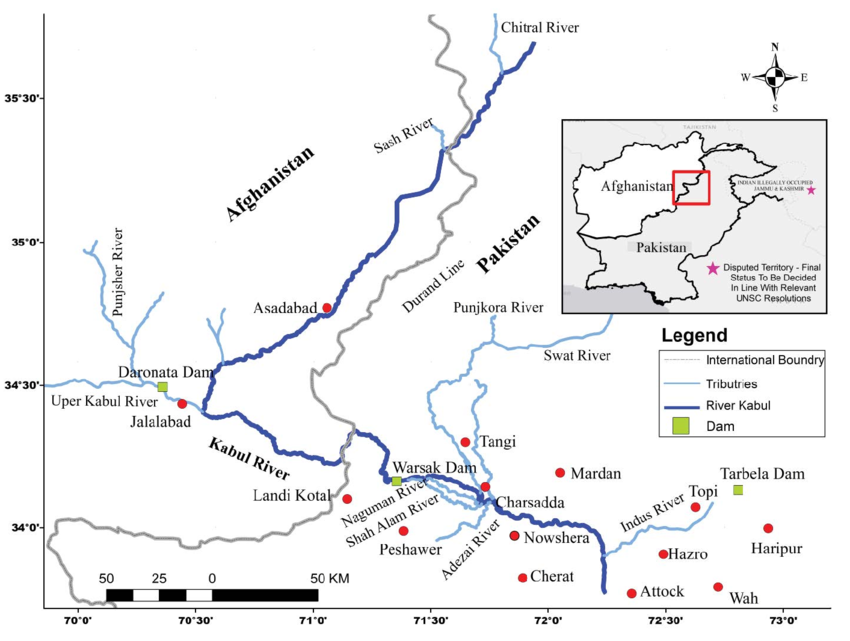
Originates in Afghanistan’s Hindu Kush region and flows into Pakistan’s Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, where it joins the Kabul River (a tributary of the Indus River).
The Kunar-Kabul River system contributes significantly to Pakistan’s water resources.
Geopolitical Implications:
Could worsen Pakistan’s water and energy crisis, as the Kunar contributes to the Indus basin.
Comes amid heightened tensions between Afghan and Pakistani border forces and mutual accusations (e.g., Pakistan blaming Kabul for harbouring Tehrik-i-Taliban Pakistan militants).
Pakistan could face a “squeeze” on its river waters from India in the east (Indus Waters suspension) and Afghanistan in the west (Kunar River dams).
Chitral / Kunar River System
Overview
The Chitral River (in Pakistan) and the Kunar River (in Afghanistan) are the same river known by two names in different regions.
It is a major tributary of the Kabul River, which ultimately joins the Indus River in Pakistan — making it part of the Indus Basin System.
It later merges with Kabul river in Nangahar Province of Afghanistan
Geographical Facts
Feature | Description |
Origin | Chiantar Glacier in the Hindu Kush Mountains (at the border of Gilgit-Baltistan and Chitral, Pakistan) |
Total Length | 480 km (300 miles) |
Countries Covered | Pakistan 🇵🇰 and Afghanistan 🇦🇫 |
Provinces/Regions | Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (Pakistan); Nuristan, Kunar, and Nangarhar (Afghanistan) |
Mouth (confluence) | Joins the Kabul River near Jalalabad, Afghanistan |
Ultimate Drainage | Flows into the Indus River at Attock, Pakistan |
Major Tributaries | Shishi River (left), Lotkoh River, Landai Sin River, Pech River (right) |
Basin Area | ~26,000 km² |
Primary Source of Water | Glacial and snowmelt from the Hindu Kush Mountains |
Hydrological Significance
Around 60–70% of the annual discharge of the Kunar River originates from Chitral (Pakistan).
Plays a vital role in Pakistan’s water security, as it feeds the Kabul River, a key tributary of the Indus.
The river supports irrigation, hydropower, and local livelihoods on both sides of the border.
Prelims Practice MCQ
Which of the following statements is/are correct?
The Chitral River originates in Afghanistan.
The Kunar River joins the Kabul River near Jalalabad.
The river is fed mainly by melting glaciers of the Hindu Kush.
Select the correct answer:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only ✅
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
It originates from the Chiantar glacier, located at the border of Gilgit Baltistan and Chitral in Pakistan.
Q. Which of the following statements about the Kunar River is/are correct?
It originates in Afghanistan and flows into Pakistan.
It merges with the Kabul River before joining the Indus.
It is entirely within Pakistan’s territory.
Select the correct answer:
(a) 2 only ✅
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
