Metagenomics
 Click to view full image
Click to view full image
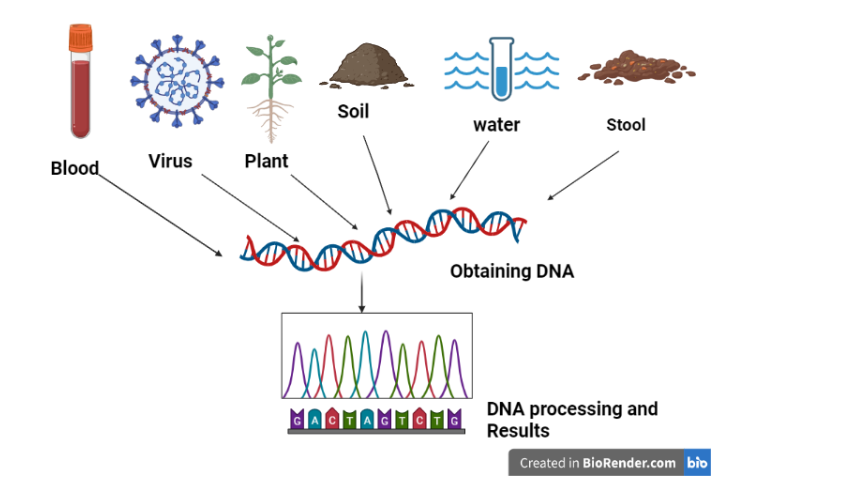
Metagenomics is the study of genetic material recovered directly from environmental samples — without needing to isolate or culture individual organisms.
In simple terms:
Metagenomics allows scientists to study all the microorganisms (bacteria, viruses, fungi, archaea, etc.) present in a sample — such as soil, water, or the human gut — as a community by analyzing their collective DNA.
Key Features of Metagenomics:
-
Culture-independent:
-
Traditional microbiology requires growing organisms in the lab.
-
Metagenomics bypasses this, capturing microbes that can't be cultured (which are the majority).
-
-
Uses high-throughput DNA sequencing:
-
Techniques like next-generation sequencing (NGS) allow researchers to read billions of DNA fragments quickly.
-
-
Gives insights into:
-
Microbial diversity (What microbes are present?)
-
Functional potential (What genes and metabolic pathways are present?)
-
Microbial interactions and how they affect the environment or host (like in the human gut).
-
Applications:
-
Human health: Understanding the gut microbiome’s role in digestion, immunity, obesity, diabetes, etc.
-
Agriculture: Studying soil microbes for crop health.
-
Environmental science: Monitoring water pollution or biodegradation.
-
Biotechnology: Finding novel enzymes or antibiotics from microbial communities.
Example:
In the kombucha, researchers used metagenomic tools to analyze stool samples. This helped them identify changes in the gut microbial composition — like increases in Akkermansia or Prevotella — in response to kombucha consumption.
