NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar (NISAR)
Launch Details
-
Launch Site: Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Sriharikota, Andhra Pradesh
-
Launch Vehicle: GSLV-F16
-
Orbit: Sun-synchronous orbit
-
Weight: 2,392 kg
-
Orbit Injection: Successful at 18 minutes post-launch
Mission Profile
-
Mission Type: Earth Observation Satellite
-
Mission Life: 5 years
-
Agencies Involved: Joint venture between ISRO (India) and NASA (USA)
-
Significance: First satellite jointly developed by NASA and ISRO
Technical Features
-
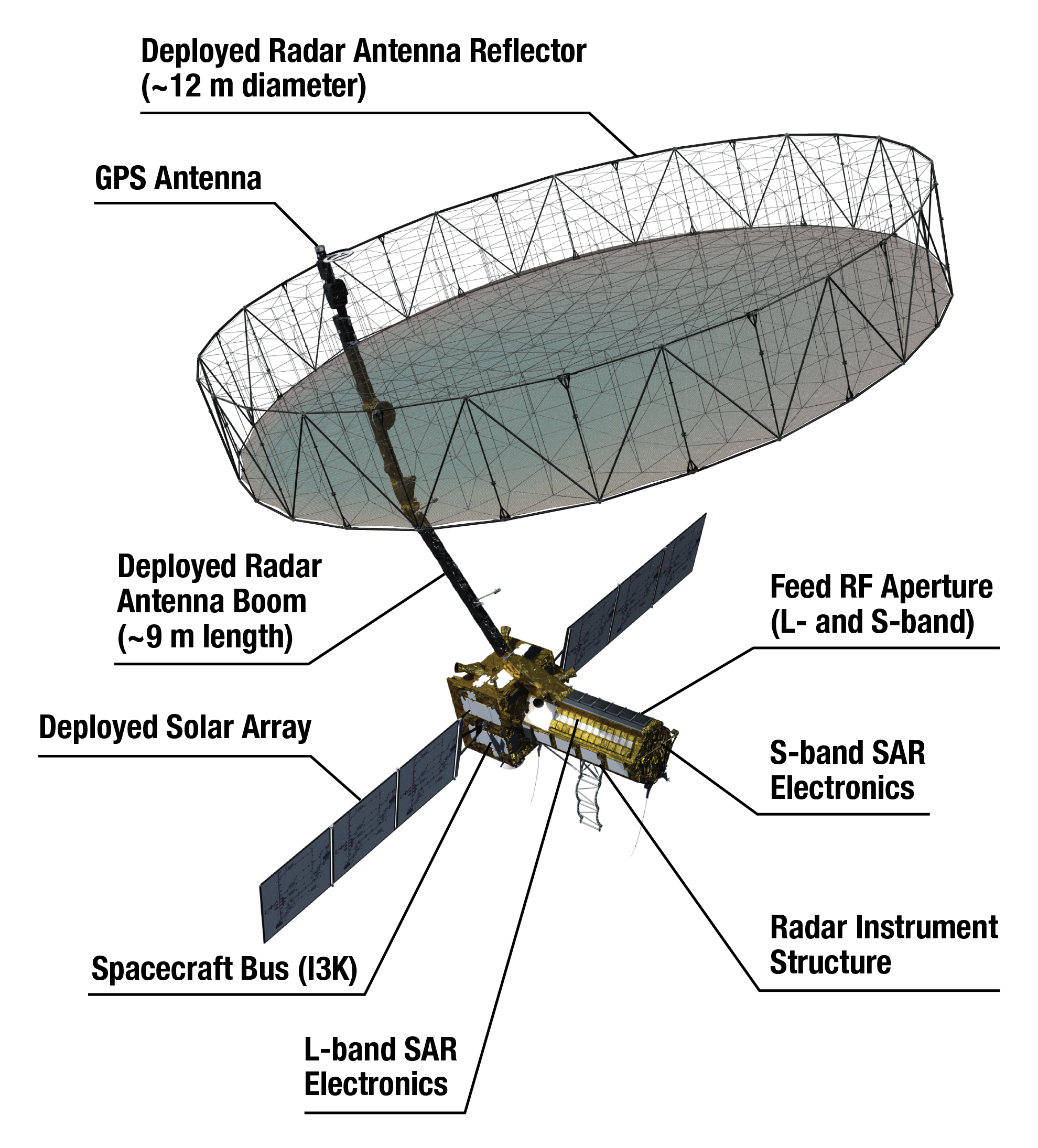
Radar System: Dual-frequency Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR)
-
NASA's L-band SAR
-
ISRO's S-band SAR
-
-
Antenna:
-
12-metre unfurlable mesh reflector (NASA)
-
Integrated with ISRO’s modified I3K satellite bus
-
-
Technology Used: SweepSAR – enables wide swathe observation with high resolution
-
Swathe Width: 242 km
-
Repeat Cycle: Every 12 days
-
All-weather, Day-Night Imaging
Applications
-
Disaster Management: Earthquakes, floods, landslides
-
Infrastructure Monitoring
-
Agriculture: Farmland mapping, crop output prediction
-
Environmental Monitoring:
-
Ground deformation
-
Ice sheet movement
-
Vegetation dynamics
-
Sea ice classification
-
Soil moisture changes
-
Surface water mapping
-
Shoreline and storm monitoring
-
Ship detection
-
Development Contributions
-
NASA (JPL):
-
Radar antenna reflector & boom
-
L-band SAR
-
Engineering payload
-
-
ISRO:
-
Spacecraft bus
-
Solar arrays
-
S-band SAR
-
GSLV-F16 launch vehicle
-
Significance
-
Strengthens Indo-US Space Collaboration
-
Enhances India’s Earth Observation Capability
-
Pioneers Dual-frequency SAR from Space
