PUNCH Mission (NASA) and Space weather
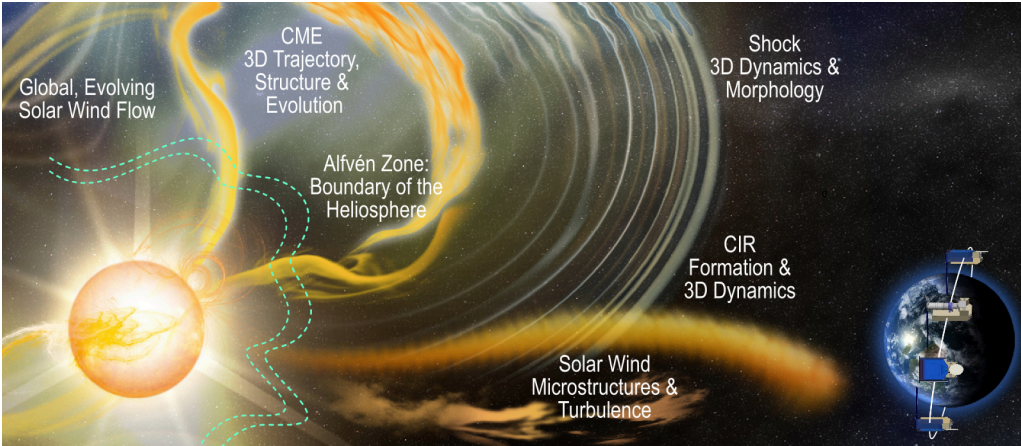
About PUNCH Mission (NASA)
Full form: Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere (PUNCH)
Launched: 2025 (by NASA)
Objective: To study the Sun’s corona and the solar wind as a single connected system.
Key function:
Makes the “invisible solar wind visible.”
Uses polarimetric imaging to observe faint structures extending from the Sun into interplanetary space.
Significance: Helps understand how the solar corona transitions into the solar wind, which affects space weather throughout the solar system.
- It is the first mission designed to measure the corona and solar wind in three dimensions by studying the polarization of light, which is the direction light travels after it has been scattered by particles.
Mission Composition
Number of Satellites: 4 small (suitcase-sized) satellites.
Orbit: Distributed around Earth along the day–night line to capture a full view of the Sun’s corona and solar wind.
Instruments:
3 Wide Field Imagers (WFIs): Image corona and solar wind up to 45° from the Sun.
1 Narrow Field Imager (NFI): Focuses on regions closest to the Sun.
All four cameras will synchronize to form a seamless panoramic view of the corona–solar wind interface.
Scientific Objectives
Understand transition: How the Sun’s outer atmosphere (corona) accelerates and becomes the solar wind.
Study structure formation: How structures in the solar wind (such as density variations, magnetic fluctuations) are created.
Track coronal mass ejections (CMEs): Observe their evolution and propagation through the solar system.
Assess space weather impacts: How the Sun’s activity influences Earth’s magnetosphere, satellites, and astronauts.
Unique Features
Artificial Eclipse: PUNCH will create an artificial eclipse to continuously image the upper corona and CMEs—unlike Earth-based observations that require total solar eclipses.
First Mission Using Polarized Light in 3D Mapping:
Uses polarimetry (measurement of polarization of scattered sunlight by electrons).
Enables creation of 3D maps of the corona and inner heliosphere.
Uses polarizing filters, similar to polarized sunglasses.
High Sensitivity & Wide Field View: Offers unprecedented resolution and depth, surpassing earlier instruments.
Importance of Studying Space Weather
a. Definition
Space weather refers to the varying environmental conditions in space due to the Sun’s activity, including phenomena like solar flares, coronal mass ejections (CMEs), and solar wind variations.
b. Why It Matters
Protection of Human Technology:
Solar storms can damage satellites, power grids, communication systems, and navigation networks.
Human Safety in Space:
Astronauts are vulnerable to solar radiation and charged particles during solar events.
Impact on Aviation and GPS:
Polar flights and navigation systems are disrupted during solar flares.
Economic Implications:
Space weather-induced outages can cost billions globally.
Scientific Understanding:
Helps improve forecasting models and design better shielding technologies for space missions.
The Current Solar Phase
The Sun is currently in the Solar Maximum phase — a period of high solar activity within the 11-year solar cycle.
Solar Maximum: Characterised by increased sunspots, solar flares, and CMEs.
According to Dr. DeForest:
“We cannot predict when an ejection will happen, but we can predict that ejections will happen over a period.”
Indicates predictable trends but unpredictable timing — requiring continuous observation.
The Sun is expected to become quieter in about five years (around 2030).
Scientific Goals of PUNCH
Unify corona and heliosphere observation: Understand how solar material accelerates and becomes solar wind.
Track solar disturbances: Visualise CMEs and their journey toward Earth.
Advance space weather forecasting: Provide real-time data for global forecasting centres.
Contribute to planetary protection: Help safeguard human space assets, astronauts, and terrestrial systems.
Prelims Practice MCQ
Q. With reference to NASA’s PUNCH Mission, consider the following statements:
It aims to study the transition between the Sun’s corona and the solar wind as a unified system.
It uses polarimetric imaging techniques to visualise the solar wind.
It is jointly conducted by NASA and ISRO under the Artemis programme.
It seeks to monitor the Sun during its solar minimum phase.
Which of the above statements are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1, 3, and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, and 4
Answer: (a)
Explanation:
Statements 1 & 2: Correct — core aims and methods of the PUNCH mission.
Statement 3: Incorrect — PUNCH is a NASA-only mission, not part of Artemis.
Statement 4: Incorrect — Launched during solar maximum, not minimum.
