RATIONALISATION OF ROYALTY RATES FOR CRITICAL MINERALS
Context
To reduce import dependence, strengthen supply chain security, and promote domestic exploration, the Union Cabinet approved rationalised royalty rates for four critical minerals:
Graphite
Caesium
Rubidium
Zirconium
Aim: encourage auctioning of mineral blocks, attract private investment, and support India’s Critical Mineral Strategy.
Why was rationalisation needed?
Earlier royalty rates were non-competitive, discouraging bidders.
For some minerals, royalty rates were unclear or too high, making mining financially unattractive.
India seeks to secure supply chains for battery minerals, electronics, nuclear applications, energy transition technologies.
New Royalty Structure
A. Graphite (major change)
Earlier: royalty on per-tonne basis (fixed amount per unit weight).
Now: ad valorem basis (percentage of sale price).
New rates:
Graphite (<80% fixed carbon): 4% of average sale price
Graphite (≥80% carbon): 2% of average sale price
Higher-grade graphite gets lower royalty to promote high-quality extraction.
B. Caesium
Royalty = 2% of average sale price
Basis: metal content extracted
C. Rubidium
Royalty = 2% of average sale price
Basis: metal contained in ore
D. Zirconium
Royalty = 1% of average sale price
Favourable rate to encourage auctions in nuclear and refractory material sector.
Benefits Expected
Promote Auctions
Rational royalty makes bidding more rational and competitive.
Encourages auction of blocks for caesium, rubidium, zirconium which earlier saw limited interest.
Reduce Import Dependence
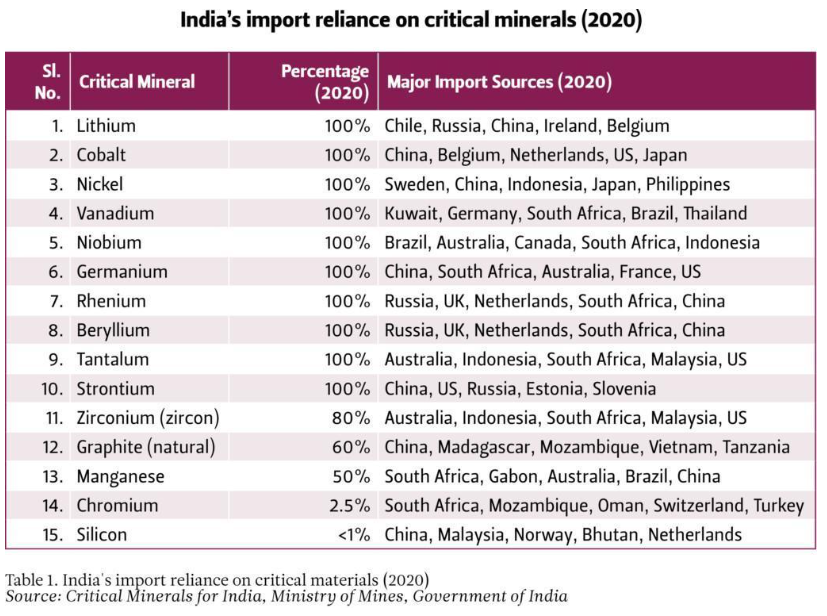
India currently imports large quantities of graphite, zirconium, and traces of caesium, rubidium.
Boost Strategic Industries
Graphite → batteries, electric vehicles, refractories.
Caesium → atomic clocks, drilling fluids, optical instruments.
Rubidium → electronics, biomedical research.
Zirconium → nuclear reactors, ceramics, space tech.
Support Critical Minerals Mission
Aligned with India's Critical Minerals for Energy Transition strategy.
Prelims Practice MCQs
Q. Caesium, rubidium, and zirconium royalty rates are based on:
A. The total weight of ore extracted
B. The specific metal content within the ore
C. The grade of ore decided by State governments
D. A per-hectare production levy
Answer: B
Royalty is charged on metal content, not total ore weight.
Q. Zirconium is most crucial for which sector in India?
A. Fertilizer production
B. Nuclear energy
C. Cement manufacturing
D. Textile bleaching
Answer: B
Zirconium is essential in nuclear reactors, corrosion-resistant cladding materials, and high-temperature ceramics.
