Resignation of the 14th Vice-President of India
Vice-President of India – Term, Vacancy, Powers and Functions:
The office of vice president is the second-highest constitutional office after the president and ranks second in the order of precedence and first in the line of succession to the presidency
Term and Vacancy
-
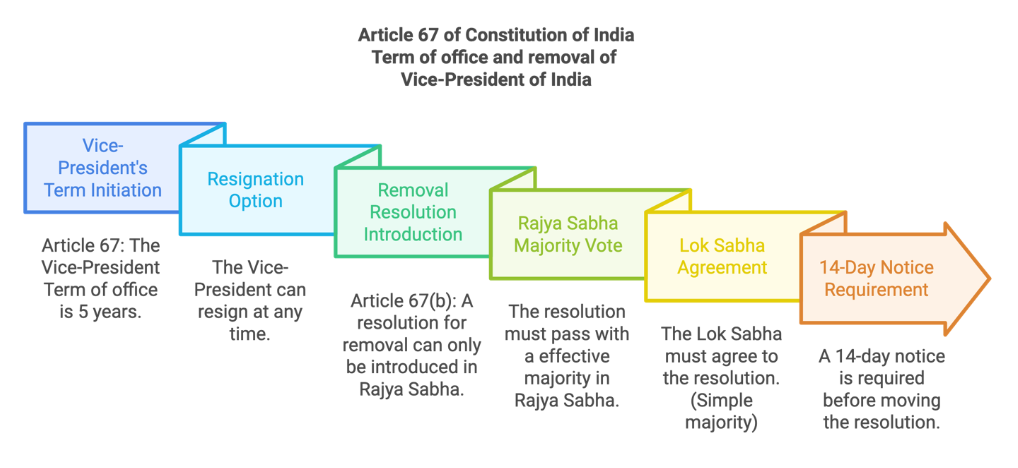
The Vice-President (VP) holds office for five years but can resign earlier by writing to the President.
-
Removal is possible via a resolution passed by:
-
Effective majority (majority of all the members of the House, not just those present and voting)
in the Rajya Sabha (initiated here only), and Simple majority in the Lok Sabha
-
With 14 days’ notice, and no specific grounds are required.
- Unlike the process for removing the President, the Constitution does not outline specific reasons for removing the Vice President.
-
Can continue beyond the term until a successor takes charge and is eligible for re-election any number of times.
-
Dr. S. Radhakrishnan was re-elected for a second term.
Vacancy Causes:
-
Expiry of tenure
-
Resignation
-
Removal
-
Death (e.g., Krishna Kant 1st to die in office)
-
Disqualification or void election
-
If term expires: election before expiry.
-
If vacancy due to other reasons: election as soon as possible.
-
Newly elected VP holds a full five-year term.
Powers and Functions
-
Ex-officio Chairman of Rajya Sabha:
-
Similar to Speaker of Lok Sabha.
-
Like the American VP who is Chairman of the Senate.
-
-
Acts as President:
-
In case of President’s vacancy (resignation, removal, death, etc.),
-
Can act up to 6 months, until new President is elected.
-
Temporarily discharges duties when President is ill or absent.
-
During this time, the Deputy Chairman of Rajya Sabha handles Rajya Sabha duties.
-
Emoluments & Privileges
-
No separate salary as VP.
-
Gets salary as Chairman of Rajya Sabha: ₹4 lakh/month .
-
Pension: 50% of salary (per 2008 amendment).
-
Entitled to allowances, residence, medical and travel facilities.
-
When acting as President, receives President's salary and perks.
Comparison with American VP
-
Indian VP becomes Acting President only.
-
American VP becomes President for the full remaining term.
-
Indian VP’s role is seen as limited and largely ceremonial, leading some to call it “His Superfluous Highness”.
-
Still, the post ensures political continuity in the Indian system.
