Shortage of Medical Radioisotopes
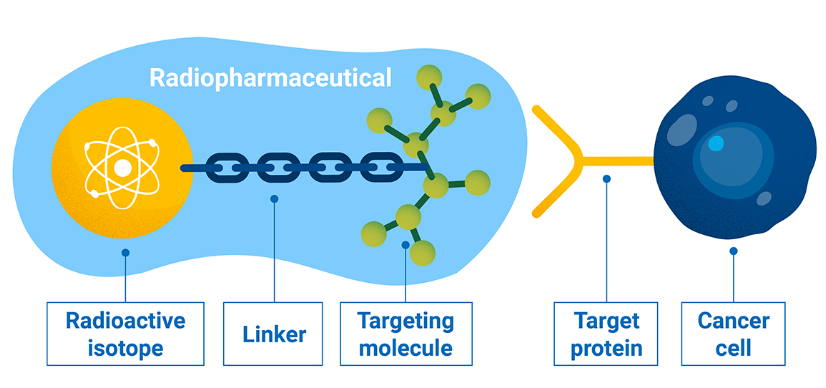
-
Full form: Board of Radiation & Isotope Technology.
The Board of Radiation and Isotope Technology (BRIT) is a unit under the Department of Atomic Energy (DAE), headquartered in Navi Mumbai, India. It focuses on developing applications of radioisotope and radiation technology.
BRIT collaborates with the Bhabha Atomic Research Centre (BARC) and Nuclear Power Corporation of India Limited (NPCIL) to support research and nuclear power generation. Its pharmaceuticals and laboratories are located at the BRIT/BARC Vashi Complex in Navi Mumbai.
| Isotope | Qty Produced (Curie) | Supply Meets Demand? | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lutetium-177 (Lu-177) | 1000–1200 | Yes (85–90% met) | Small 10–15% gap. Used in targeted cancer therapy. |
| Iodine-131 (I-131) | 1000–1200 | No | Used for thyroid disorders/cancer. |
| Molybdenum-99 (Mo-99) (parent of Tc-99m) | 8000–10000 | No | Critical for diagnostic imaging. Significant shortage. |
| Fluorine-18 (F-18) | 300–400 | No | Short half-life (110 min) limits distribution to nearby hospitals only. |
| Gallium-68 (Ga-68) | — | Yes | No demand-supply mismatch. |
-
F-18: Half-life of 110 min → logistical constraints; can only supply nearby hospitals (MCF Parel, Cyclon-30).
-
Mo-99: Significant demand-supply gap.
-
Lu-177: Small shortfall despite high production coverage.
-
PPP-based Isotope Reactor Project – Bhabha Atomic Research Centre (BARC).
-
Status: In-principle approval obtained; DPR under review.
-
Capacity: 0.5 MCi radioisotope production.
-
Expected Start: Around 2035.
-
-
Tata Memorial Centre (TMC) Expansion – Nuclear medicine facilities in Tier-2 & Tier-3 cities:
-
Tier-2: New Chandigarh, Visakhapatnam, Bhubaneswar, Guwahati, Varanasi, Muzaffarpur.
-
Tier-3: Sangrur (Punjab).
-
