Super Pollutants
Why in news :
Recoolit, a climate-tech startup in Indonesia, is combating climate change by capturing and destroying refrigerants (particularly HFCs) — potent greenhouse gases used in air conditioners, refrigerators, and vehicles.
Super pollutants are a group of short-lived climate pollutants (SLCPs) that have very high global warming potential (GWP) — often hundreds to thousands of times more potent than CO₂ over short time frames (usually 20 years), but remain in the atmosphere for a shorter duration.
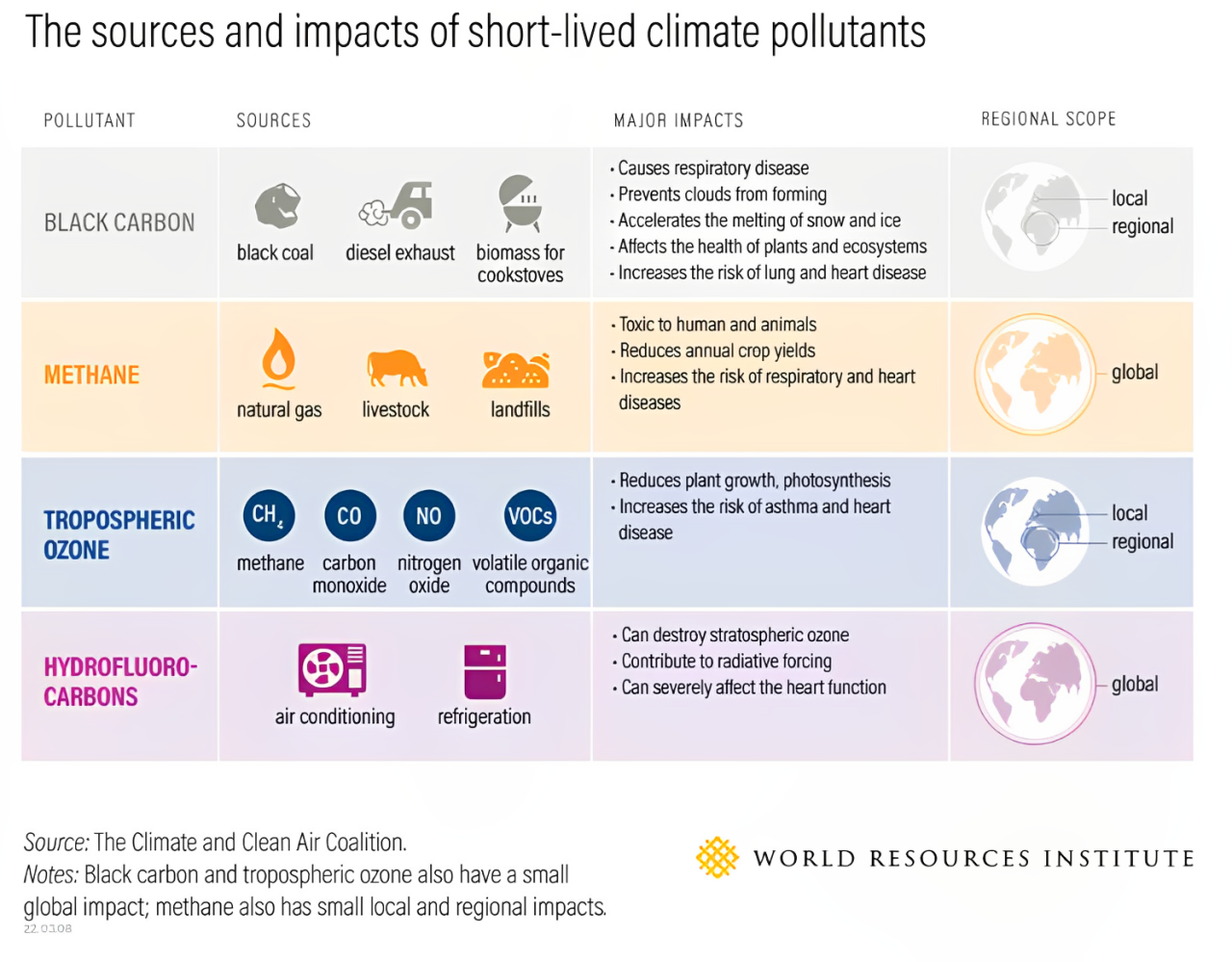
Key Super Pollutants:
| Pollutant | Source | Global Warming Potential (GWP, 20-year) | Other Impacts |
|---|---|---|---|
| Methane (CH₄) | Agriculture, landfills, oil & gas leaks | ~84–87 | Contributes to ground-level ozone, respiratory illnesses |
| Black Carbon (Soot) | Diesel engines, biomass burning | ~900–3,200 | Major cause of glacier melt, health hazard |
| Hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) | ACs, refrigerators | Up to 12,000 | No ozone depletion, but high GWP |
| Tropospheric Ozone (O₃) | Secondary pollutant from fossil fuels & methane | — | Damages crops, affects lungs |
Why are They Important?
-
Short-lived, high-impact: Unlike CO₂, which stays in the atmosphere for centuries, super pollutants can be removed quickly — offering rapid climate benefits.
-
Mitigation can reduce global warming by ~0.5°C by 2050 (UNEP estimate).
-
Health and crop benefits: Reducing super pollutants improves air quality and agricultural yields.
India and Global Action:
-
Kigali Amendment (2016) to Montreal Protocol – targets HFCs.
-
India Cooling Action Plan (2019) – promotes low-GWP refrigerants.
-
National Clean Air Programme (NCAP) – targets black carbon and methane indirectly.
-
Global Methane Pledge (COP26) – India is not a signatory yet but has domestic methane reduction initiatives via waste and livestock management.
