Venezuela crisis and India’s energy security
Context
The recent U.S. military action in Venezuela and statements regarding control over Venezuelan oil have raised concerns globally. However, India’s energy security remains largely insulated from these developments.
Key facts
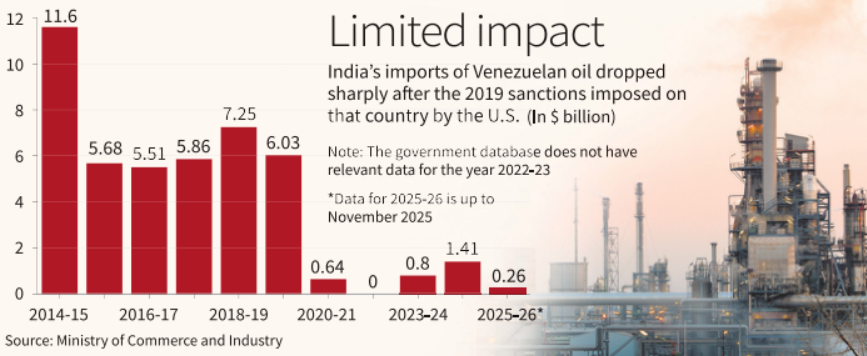
India’s crude oil import from Venezuela (FY 2025–26 till Nov):
$255.3 million, about 0.3% of total oil importsPeak import (2013): ~$13 billion
Trend since 2019: Sharp decline due to U.S. sanctions and threat of secondary sanctions
Venezuela’s share:
~3.5% of OPEC exports
~1% of global oil supply
Why India’s energy security is not significantly affected
1. Marginal trade exposure
India’s dependence on Venezuelan crude is negligible, making supply disruptions economically insignificant.
2. Sanctions already factored in
India has gradually disengaged since 2019
Trade disruption is not a new shock, but an already-adjusted reality
3. Nature of Venezuelan crude
Venezuelan oil is heavy and extra-heavy crude
Requires specialized refineries
Most Indian refineries are optimized for Middle Eastern crude blends
4. Diversified import basket
India sources crude from:
West Asia (Saudi Arabia, Iraq, UAE)
Russia
Africa
Latin America (limited)
This diversification cushions geopolitical shocks.
OPEC angle
Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) influences prices and supply
Despite being an OPEC member, Venezuela’s actual production is low
Hence, instability in Venezuela does not materially affect OPEC’s overall output strategy
What is OPEC
Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries is an intergovernmental organization
Objective:
Enable cooperation among major oil-producing and oil-dependent countries
Collectively influence global oil markets
Maximize returns from petroleum resources
Operates through coordinated production policies.
Foundation and origin
Founded: 14 September 1960
Place: Baghdad (Iraq)
Founding members (5):
Iran
Iraq
Kuwait
Saudi Arabia
Venezuela
Membership
Current members: 12 countries
Membership is dominated by:
Middle Eastern
African
Latin American oil producers
Members pay equal membership fees irrespective of production size.
OPEC membership (as of January 2026)
Total members: 12
Current member countries
Africa (6):
Algeria
Republic of the Congo
Equatorial Guinea
Gabon
Libya
Nigeria
Middle East (5):
Iran
Iraq
Kuwait
Saudi Arabia
United Arab Emirates
South America (1):
Venezuela
Africa has more OPEC members than the Middle East
Countries no longer in OPEC
Angola – Withdrew effective 1 January 2024
Qatar – Left in January 2019
Ecuador – Not a current member
Indonesia – Not a current member
Membership in OPEC is not permanent
Share in global oil economy
Global oil production share (2022): ~38%
Global proven oil reserves: ~79.5% located in OPEC countries
Middle East share:
~67.2% of OPEC’s total proven oil reserves
Key inference:
OPEC’s power lies more in reserves and spare capacity than current production alone
Organisational structure
OPEC Conference (Supreme authority)
Highest decision-making body
Composed of:
Delegations headed by oil ministers of member countries
Functions:
Sets overall policy
Decides production targets
Meetings:
At least twice a year
Extraordinary sessions when required
Secretariat
Headed by OPEC Secretary General
Executes decisions of the Conference
Provides research, data, and coordination support
Headquarters
Vienna, Austria
All ordinary Conference meetings are held here
Decision-making principles
Unanimity
One member, one vote
Equal budget contribution despite unequal production capacities
(voting power is not proportional to output)
Saudi Arabia’s special position
Saudi Arabia is:
Largest oil exporter within OPEC
Possesses substantial spare production capacity
Acts as:
Swing producer — increases or cuts output to stabilize global prices
Hence regarded as:
OPEC’s de facto leader (informal, not institutional)
Prelims Practice MCQs
Q. The original founding members of OPEC include:
Iran
Iraq
Kuwait
Saudi Arabia
Qatar
Venezuela
Select the correct answer using the code below:
(a) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 6 only
(b) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 only
(c) 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6 only
(d) 1, 3, 4, 5 and 6 only
Answer: (a)
Explanation:
Qatar was not a founding member.
Q. According to recent estimates, OPEC countries account for approximately:
(a) 25% of global oil production and 40% of proven reserves
(b) 38% of global oil production and about 80% of proven reserves
(c) 50% of global oil production and 50% of proven reserves
(d) 60% of global oil production and 90% of proven reserves
Answer: (b)
Explanation:
OPEC controls a much higher share of reserves than production.
