What are powertrains?
A powertrain is the complete system in a vehicle that generates power and delivers it to the wheels, enabling the vehicle to move.
It includes:
Energy source (fuel tank or battery)
Engine or motor (or both)
Transmission system
Drivetrain components (shafts, differential, axles)
In simple terms, the powertrain decides how a car is powered and how efficiently that power is used.
Major types of powertrains
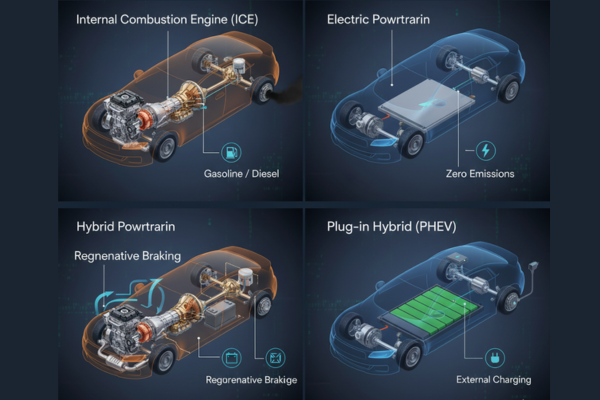
1. Internal combustion engine (ICE) powertrains
These use fossil fuels and have been dominant historically.
Petrol (gasoline)
Smoother, quieter, lower upfront cost, higher emissions than hybrids.Diesel
Higher torque, better fuel efficiency for long distances, but stricter emission norms.CNG / LPG
Cleaner than petrol/diesel, lower running cost, limited refuelling infrastructure.
2. Hybrid powertrains
These combine an internal combustion engine with an electric motor and battery.
Mild hybrid
Electric motor assists the engine but cannot drive the car alone.Full hybrid (strong hybrid)
Vehicle can run on:engine alone
electric motor alone
both together
No external charging needed.
Plug-in hybrid (PHEV)
Battery can be charged externally and offers longer electric-only range.
Why important for India:
Better fuel efficiency
Lower emissions
No charging anxiety like pure EVs
3. Electric vehicle (EV) powertrain
Uses only an electric motor and battery
Zero tailpipe emissions
High efficiency, low running cost
Dependent on charging infrastructure and battery costs
4. Emerging and alternative powertrains
Flex-fuel engines (ethanol-petrol blends)
Hydrogen fuel cell (long-term, still limited in India)
Prelims Practice MCQs
Q. Consider the following statements about hybrid powertrains:
They combine an internal combustion engine with an electric motor.
All hybrid vehicles require external charging.
Hybrid powertrains help reduce fuel consumption and emissions.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 3 only
B. 1 only
C. 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
Answer: A
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct.
Statement 2 is incorrect because full hybrids do not require external charging.
Statement 3 is correct due to regenerative braking and electric assistance.
Q. Plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) differ from full hybrids because they:
A. Cannot run on electric power alone
B. Use hydrogen as a fuel
C. Have batteries that can be charged externally
D. Do not use internal combustion engines
Answer: C
Explanation:
PHEVs have larger batteries and can be charged from an external power source, allowing longer electric-only driving ranges.
